Question # 1
Refer to Exhibit:
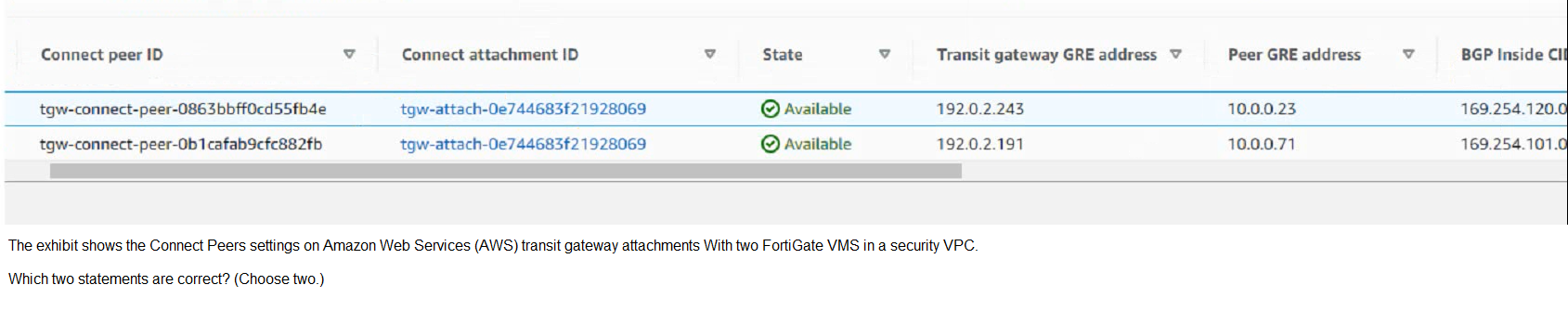
|
| A. The peer GRE address is the FortiGate external interface IP address.
| | B. The Transit Gateway GRE address is auto-generated
| | C. The BGP inside CIDR blocks can be any CIDR block with /29
| | D. The Peer GRE address is the FortiGate internal interface IP address |
A. The peer GRE address is the FortiGate external interface IP address.
B. The Transit Gateway GRE address is auto-generated
Explanation:
A. The peer GRE address is the FortiGate external interface IP address. This is the IP
address of the FortiGate interface that is connected to the transit gateway attachment
subnet1. This IP address is used to establish the GRE tunnel between the FortiGate and
the transit gateway2.
B. The Transit Gateway GRE address is auto-generated. This is the
IP address of the transit gateway that is used to establish the GRE tunnel with the
FortiGate2. This IP address is automatically assigned by AWS from the Transit Gateway
CIDR range that you specify when you create the Connect attachment3.
The other options are incorrect because:
The BGP inside CIDR blocks cannot be any CIDR block with /29. They must be a
/29 CIDR block from the 169.254.0.0/16 range for IPv4, or a /125 CIDR block from
the fd00::/8 range for IPv64. These are the inside IP addresses that are used for
BGP peering over the GRE tunnel4.
The Peer GRE address is not the FortiGate internal interface IP address. The
internal interface IP address is used to route traffic from the FortiGate to the VPC
subnet where the third-party appliance (such as SD-WAN) is located1. The Peer
GRE address is used to route traffic from the FortiGate to the transit gateway over
the GRE tunnel2.
Question # 2
| Refer to the exhibit |
| A. Use the terraform destroy command
| | B. Use the terraform validate command.
| | C. Use the terraform destroy all command.
| | D. The administrator must manually delete the Linux server. |
A. Use the terraform destroy command
D. The administrator must manually delete the Linux server.
A. Use the terraform destroy command. This command is used to remove all the resources
that were created using the Terraform configuration1. It is the opposite of the terraform
apply command, which is used to create resources. The terraform destroy command will
first show a plan of what resources will be destroyed, and then ask for confirmation before
proceeding. The command will also update the state file to reflect the changes.
D. The
administrator must manually delete the Linux server. This is because the Linux server was
not deployed using Terraform, but using AWS Marketplace2. Therefore, Terraform does
not have any information about the Linux server in its state file, and cannot manage or
destroy it. The administrator will have to use the AWS console or CLI to delete the Linux
server manually.
The other options are incorrect because:
There is no terraform validate command. The correct command is terraform plan,
which is used to show a plan of what changes will be made by applying the
configuration3. However, this command does not delete any resources, it only
shows what will happen if terraform apply or terraform destroy is run.
There is no terraform destroy all command. The correct command is terraform
destroy, which will destroy all the resources in the current configuration by
default1. There is no need to add an all argument to the command.
Question # 3
| You are tasked with deploying a FortiGate HA solution in Amazon Web Services (AWS)
using Terraform What are two steps you must take to complete this deployment? (Choose
two.) |
| A. Enable automation on the AWS portal.
| | B. Create an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user With permissions.
| | C. Use CloudSheIl to install Terraform.
| | D. Create an AWS Active Directory user with permissions. |
B. Create an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user With permissions.
C. Use CloudSheIl to install Terraform.
Explanation:
To deploy a FortiGate HA solution in AWS using Terraform, you need to create an AWS
IAM user with permissions to access the AWS resources and services required by the
FortiGate-VM. You also need to use CloudShell to install Terraform, which is a tool for
building, changing, and versioning infrastructure as code.
Question # 4
| Which two Amazon Web Services (AWS) features support east-west traffic inspection
within the AWS cloud by the FortiGate VM? (Choose two.) |
| A. A NAT gateway with an EIP
| | B. A transit gateway with an attachment
| | C. An Internet gateway with an EIP
| | D. A transit VPC |
B. A transit gateway with an attachment
D. A transit VPC
Explanation:
The correct answer is B and D. A transit gateway with an attachment and a transit VPC
support east-west traffic inspection within the AWS cloud by the FortiGate VM.
According to the Fortinet documentation for Public Cloud Security, a transit gateway is a
network transit hub that connects VPCs and on-premises networks. A transit gateway
attachment is a resource that connects a VPC or VPN to a transit gateway. By using a
transit gateway with an attachment, you can route traffic from your spoke VPCs to your
security VPC, where the FortiGate VM can inspect the traffic1.
A transit VPC is a VPC that serves as a global network transit center for connecting
multiple VPCs, remote networks, and virtual private networks (VPNs).By using a transit
VPC, you can deploy the FortiGate VM as a virtual appliance that provides network security
and threat prevention for your VPCs2.
The other options are incorrect because:
A NAT gateway with an EIP is a service that enables instances in a private subnet
to connect to the internet or other AWS services, but prevents the internet from
initiating a connection with those instances. A NAT gateway with an EIP does not
support east-west traffic inspection within the AWS cloud by the FortiGate VM3.
An Internet gateway with an EIP is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly
available VPC component that allows communication between instances in your
VPC and the internet. An Internet gateway with an EIP does not support east-west
traffic inspection within the AWS cloud by the FortiGate VM4.
Question # 5
| Refer to the exhibit |
| A. There is no connection between VPC A and VPC B.
| | B. There is no elastic IP address attached to FortiGate in the Security VPC.
| | C. The Transit Gateway BGP IP address is incorrect.
| | D. There is no internet gateway attached to the Spoke VPC A. |
D. There is no internet gateway attached to the Spoke VPC A.
Explanation: This is because the Linux1 EC2 instance is not accessible directly from the
internet using its public IP address in AWS.
An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC
component that allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
Without an internet gateway, the Linux1 EC2 instance cannot receive or send traffic to or
from the internet, even if it has a public IP address assigned to it.
To fix this issue, you need to attach an internet gateway to the Spoke VPC A and configure
a route table that directs internet-bound traffic to the internet gateway. You also need to
ensure that the Linux1 EC2 instance has a security group that allows inbound and
outbound traffic on the desired ports.
Question # 6
| Refer to the exhibit. |
| A. Add both Associations and Propagations in the second TGW route table.
| | B. Delete the both Connect and Transport attachments from the first TGW route table
| | C. Add a static route in the Routes section
| | D. In the second route table: create a propagation with the Connect attachment. |
D. In the second route table: create a propagation with the Connect attachment.
The error message indicates that the Connect attachment is already associated with
another transit gateway route table. You cannot associate the same attachment with more
than one route table. However, you can propagate the same attachment to multiple route
tables. Therefore, to fulfill your requirement of configuring a second route table for eastwest
traffic inspection between two VPCs, you need to create a propagation with the
Connect attachment in the second route table. This will allow the second route table to
learn the routes from the Connect attachment and forward the traffic to the
securityVPC1. You also need to associate the second route table with the Transport
attachment, which is the transit gateway attachment for the security VPC1.
Question # 7
| Refer to Exhibit: |
| A. The terraform plan command will deploy the rest of the resources except the service
principle details.
| | B. You cannot run the terraform apply command before the terraform plan command.
| | C. You must run the terraform init command once, before the terraform plan command
| | D. The terraform plan command makes terraform do a dry run. |
C. You must run the terraform init command once, before the terraform plan command
D. The terraform plan command makes terraform do a dry run.
Explanation:
A is incorrect because the terraform plan command will not deploy any resources
at all. It will only show the changes that would be made if the terraform apply
command was run. The error message in the exhibit indicates that the service
principal details are invalid, which means that Terraform cannot authenticate to
Azure and cannot create any resources1.
B is incorrect because you can run the terraform apply command without running
the terraform plan command first. The terraform apply command will automatically
generate a new plan and prompt you to approve it before applying it2. However,
running the terraform plan command first can help you preview the changes and
avoid any unwanted or unexpected actions.
C is correct because you must run the terraform init command once before the
terraform plan command. The terraform init command initializes a working
directory containing Terraform configuration files. It downloads and installs the
provider plugins required for your configuration, such as the Azure provider2. It
also creates a hidden directory called .terraform to store the plugin binaries and
other metadata1. Without running the terraform init command, the terraform plan
command will fail because it cannot find the required plugins or modules.
D is correct because the terraform plan command makes Terraform do a dry run.
A dry run is a simulation of what would happen if you executed a certain action,
without actually performing it. The terraform plan command creates an execution
plan, which is a description of the actions that Terraform would take to make your
infrastructure match your configuration2. The execution plan shows you what
resources will be created, modified, or destroyed, and what attributes will be
changed. The execution plan does not affect your infrastructure or state file until
you apply it with the terraform apply command1.
Question # 8
| Refer to the exhibit. |
| A. The opposite FortiGate port 1 IP address.
| | B. The public load balancer port 2 IP address
| | C. The internal load balancer port 1 IP address.
| | D. The opposite FortiGate port 2 IP address |
D. The opposite FortiGate port 2 IP address
Explanation:
In an HA active-active load balance configuration with FortiGate VMs, especially in
Microsoft Azure where FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) is used for session
synchronization, the correct configuration for thepeeripis:
D.The opposite FortiGate port 2 IP address.
HA Synchronization Requirements: FGSP requires direct communication between
the FortiGates to synchronize the session table. This synchronization typically
occurs over a dedicated HA link that connects the HA pair.
Asymmetric Traffic Considerations: FGSP allows asymmetric traffic to rejoin the
correct session by synchronizing session information, including NAT and TCP
sequence tracking between the FortiGate units in a cluster.
Configuration Specifics: For port 2, which is facing the internal load balancer,
thepeeripshould be set to the corresponding port 2 IP address of the opposite
FortiGate. This allows the internal interfaces to communicate directly with each
other for session synchronization purposes, which is crucial in an active-active
deployment to ensure sessions persist during failover scenarios.
Get 59 Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) questions Access in less then $0.12 per day.
Fortinet Bundle 1:
1 Month PDF Access For All Fortinet Exams with Updates
$200
$800
Buy Bundle 1
Fortinet Bundle 2:
3 Months PDF Access For All Fortinet Exams with Updates
$300
$1200
Buy Bundle 2
Fortinet Bundle 3:
6 Months PDF Access For All Fortinet Exams with Updates
$450
$1800
Buy Bundle 3
Fortinet Bundle 4:
12 Months PDF Access For All Fortinet Exams with Updates
$600
$2400
Buy Bundle 4
Disclaimer: Fair Usage Policy - Daily 5 Downloads
Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) Test Dumps
Exam Code: NSE7_PBC-7.2
Exam Name: Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS)
- 90 Days Free Updates
- Fortinet Experts Verified Answers
- Printable PDF File Format
- NSE7_PBC-7.2 Exam Passing Assurance
Get 100% Real NSE7_PBC-7.2 Exam Dumps With Verified Answers As Seen in the Real Exam. Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) Exam Questions are Updated Frequently and Reviewed by Industry TOP Experts for Passing NSE 7 Network Security Architect Exam Quickly and Hassle Free.
Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2 Test Dumps
Struggling with Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) preparation? Get the edge you need! Our carefully created NSE7_PBC-7.2 test dumps give you the confidence to pass the exam. We offer:
1. Up-to-date NSE 7 Network Security Architect practice questions: Stay current with the latest exam content.
2. PDF and test engine formats: Choose the study tools that work best for you.
3. Realistic Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2 practice exam: Simulate the real exam experience and boost your readiness.
Pass your NSE 7 Network Security Architect exam with ease. Try our study materials today!
Official NSE 7 Public Cloud Security exam info is available on Fortinet website at https://training.fortinet.com/local/staticpage/view.php?page=fcss_public_cloud_security
Prepare your NSE 7 Network Security Architect exam with confidence!We provide top-quality NSE7_PBC-7.2 exam dumps materials that are:
1. Accurate and up-to-date: Reflect the latest Fortinet exam changes and ensure you are studying the right content.
2. Comprehensive Cover all exam topics so you do not need to rely on multiple sources.
3. Convenient formats: Choose between PDF files and online Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) practice questions for easy studying on any device.
Do not waste time on unreliable NSE7_PBC-7.2 practice test. Choose our proven NSE 7 Network Security Architect study materials and pass with flying colors. Try Dumps4free Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) 2024 material today!
-
Assurance
Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) practice exam has been updated to reflect the most recent questions from the Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2 Exam.
-
Demo
Try before you buy! Get a free demo of our NSE 7 Network Security Architect exam dumps and see the quality for yourself. Need help? Chat with our support team.
-
Validity
Our Fortinet NSE7_PBC-7.2 PDF contains expert-verified questions and answers, ensuring you're studying the most accurate and relevant material.
-
Success
Achieve NSE7_PBC-7.2 success! Our Fortinet NSE 7 Public Cloud Security 7.2 (FCSS) exam questions give you the preparation edge.
If you have any question then contact our customer support at live chat or email us at support@dumps4free.com.
| 
