Question # 1
| A Mule application exposes an HTTPS endpoint and is deployed to three CloudHub
workers that do not use static IP addresses. The Mule application expects a high volume of
client requests in short time periods. What is the most cost-effective infrastructure
component that should be used to serve the high volume of client requests?
|
| A. A customer-hosted load balancer
| | B. The CloudHub shared load balancer
| | C. An API proxy
| | D. Runtime Manager autoscaling |
B.
The CloudHub shared load balancer
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: The CloudHub shared load balancer
*****************************************
The scenario in this question can be split as below:
>> There are 3 CloudHub workers (So, there are already good number of workers to
handle high volume of requests)
>> The workers are not using static IP addresses (So, one CANNOT use customer loadbalancing
solutions without static IPs)
>> Looking for most cost-effective component to load balance the client requests among
the workers.
Based on the above details given in the scenario:
>> Runtime autoscaling is NOT at all cost-effective as it incurs extra cost. Most over, there
are already 3 workers running which is a good number.
>> We cannot go for a customer-hosted load balancer as it is also NOT most cost-effective
(needs custom load balancer to maintain and licensing) and same time the Mule App is not
having Static IP Addresses which limits from going with custom load balancing.
>> An API Proxy is irrelevant there as it has no role to play w.r.t handling high volumes or
load balancing.
So, the only right option to go with and fits the purpose of scenario being most costeffective
is - using a CloudHub Shared Load Balancer
Question # 2
| A code-centric API documentation environment should allow API consumers to investigate
and execute API client source code that demonstrates invoking one or more APIs as part of
representative scenarios.
What is the most effective way to provide this type of code-centric API documentation
environment using Anypoint Platform?
|
| A. Enable mocking services for each of the relevant APIs and expose them via their Anypoint Exchange entry
| | B. Ensure the APIs are well documented through their Anypoint Exchange entries and API Consoles and share these pages with all API consumers
| | C. Create API Notebooks and include them in the relevant Anypoint Exchange entries
| | D. Make relevant APIs discoverable via an Anypoint Exchange entry |
C. Create API Notebooks and include them in the relevant Anypoint Exchange entries
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Create API Notebooks and Include them in the relevant Anypoint
exchange entries
*****************************************
>> API Notebooks are the one on Anypoint Platform that enable us to provide code-centric
API documentation
: https://docs.mulesoft.com/exchange/to-use-api-notebook
Bottom of Form
Top of Form
Question # 3
| A system API has a guaranteed SLA of 100 ms per request. The system API is deployed to
a primary environment as well as to a disaster recovery (DR) environment, with different
DNS names in each environment. An upstream process API invokes the system API and
the main goal of this process API is to respond to client requests in the least possible time.
In what order should the system APIs be invoked, and what changes should be made in
order to speed up the response time for requests from the process API? |
| A. In parallel, invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment and the system API deployed to the DR environment, and ONLY use the first response
| | B. In parallel, invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment and the system API deployed to the DR environment using a scatter-gather configured with a timeout, and then merge the responses
| | C. Invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment, and if it fails, invoke the system API deployed to the DR environment
| | D. Invoke ONLY the system API deployed to the primary environment, and add timeout and retry logic to avoid intermittent failures |
A. In parallel, invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment and the system API deployed to the DR environment, and ONLY use the first response
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: In parallel, invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment
and the system API deployed to the DR environment, and ONLY use the first response.
*****************************************
>> The API requirement in the given scenario is to respond in least possible time.
>> The option that is suggesting to first try the API in primary environment and then
fallback to API in DR environment would result in successful response but NOT in least
possible time. So, this is NOT a right choice of implementation for given requirement.
>> Another option that is suggesting to ONLY invoke API in primary environment and to
add timeout and retries may also result in successful response upon retries but NOT in
least possible time. So, this is also NOT a right choice of implementation for given
requirement.
>> One more option that is suggesting to invoke API in primary environment and API in DR
environment in parallel using Scatter-Gather would result in wrong API response as it
would return merged results and moreover, Scatter-Gather does things in parallel which is
true but still completes its scope only on finishing all routes inside it. So again, NOT a right
choice of implementation for given requirement
The Correct choice is to invoke the API in primary environment and the API in DR
environment parallelly, and using ONLY the first response received from one of them
Question # 4
| Version 3.0.1 of a REST API implementation represents time values in PST time using ISO
8601 hh:mm:ss format. The API implementation needs to be changed to instead represent
time values in CEST time using ISO 8601 hh:mm:ss format. When following the semver.org
semantic versioning specification, what version should be assigned to the updated API
implementation?
|
| A. 3.0.2
| | B. 4.0.0
| | C. 3.1.0
| | D. 3.0.1 |
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: 4.0.0
*****************************************
As per semver.org semantic versioning specification:
Given a version number MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, increment the:
- MAJOR version when you make incompatible API changes.
- MINOR version when you add functionality in a backwards compatible manner.
- PATCH version when you make backwards compatible bug fixes.
As per the scenario given in the question, the API implementation is completely changing
its behavior. Although the format of the time is still being maintained as hh:mm:ss and there
is no change in schema w.r.t format, the API will start functioning different after this change
as the times are going to come completely different.
Example: Before the change, say, time is going as 09:00:00 representing the PST. Now on,
after the change, the same time will go as 18:00:00 as Central European Summer Time is
9 hours ahead of Pacific Time.
>> This may lead to some uncertain behavior on API clients depending on how they are
handling the times in the API response. All the API clients need to be informed that the API
functionality is going to change and will return in CEST format. So, this considered as a
MAJOR change and the version of API for this new change would be 4.0.0
Question # 5
| What best explains the use of auto-discovery in API implementations?
|
| A. It makes API Manager aware of API implementations and hence enables it to enforce policies
| | B. It enables Anypoint Studio to discover API definitions configured in Anypoint Platform
| | C. It enables Anypoint Exchange to discover assets and makes them available for reuse
| | D. It enables Anypoint Analytics to gain insight into the usage of APIs |
A. It makes API Manager aware of API implementations and hence enables it to enforce policies
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: It makes API Manager aware of API implementations and hence enables it
to enforce policies.
*****************************************
>> API Autodiscovery is a mechanism that manages an API from API Manager by pairing
the deployed application to an API created on the platform.
>> API Management includes tracking, enforcing policies if you apply any, and reporting
API analytics.
>> Critical to the Autodiscovery process is identifying the API by providing the API name
and version.
References:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/api-auto-discovery-new-concept
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/1.x/api-auto-discovery
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/api-auto-discovery-new-concept
Question # 6
Refer to the exhibit. An organization is running a Mule standalone runtime and has
configured Active Directory as the Anypoint Platform external Identity Provider. The organization does not have budget for other system components.
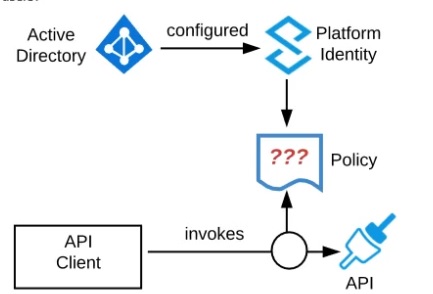
What policy should be applied to all instances of APIs in the organization to most
effecuvelyKestrict access to a specific group of internal users?
|
| A. Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory will be
configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users
| | B. Apply a client ID enforcement policy; the specific group of users will configure their client applications to use their specific client credentials
| | C. Apply an IP whitelist policy; only the specific users' workstations will be in the whitelist
| | D. Apply an OAuth 2.0 access token enforcement policy; the internal Active Directory will be configured as the OAuth server |
A.
Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory will be
configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory
will be configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users.
*****************************************
>> IP Whitelisting does NOT fit for this purpose. Moreover, the users workstations may not
necessarily have static IPs in the network.
>> OAuth 2.0 enforcement requires a client provider which isn't in the organizations system
components.
>> It is not an effective approach to let every user create separate client credentials and
configure those for their usage.
The effective way it to apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy and the internal Active
Directory will be configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users.
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/basic-authentication-ldap-concept
Question # 7
True or False. We should always make sure that the APIs being designed and developed are self-servable even if it needs more man-day effort and resources.
|
| A. FALSE
| | B. TRUE |
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: TRUE
*****************************************
>> As per MuleSoft proposed IT Operating Model, designing APIs and making sure that
they are discoverable and self-servable is VERY VERY IMPORTANT and decides the
success of an API and its application network.
Question # 8
How are an API implementation, API client, and API consumer combined to invoke and process an API?
|
| A. The API consumer creates an API implementation, which receives API invocations from
an API such that they are processed for an API client
| | B. The API client creates an API consumer, which receives API invocations from an API such that they are processed for an API implementation
| | C. The ApI consumer creates an API client, which sends API invocations to an API such that they are processed by an API implementation
| | D. The ApI client creates an API consumer, which sends API invocations to an API such that they are processed by an API implementation |
C.
The ApI consumer creates an API client, which sends API invocations to an API such that they are processed by an API implementation
Explanation:
Explanation
Correct Answer: The API consumer creates an API client, which sends API invocations to
an API such that they are processed by an API implementation
*****************************************
Terminology:
>> API Client - It is a piece of code or program the is written to invoke an API
>> API Consumer - An owner/entity who owns the API Client. API Consumers write API
clients.
>> API - The provider of the API functionality. Typically an API Instance on API Manager
where they are managed and operated.
>> API Implementation - The actual piece of code written by API provider where the
functionality of the API is implemented. Typically, these are Mule Applications running on
Runtime Manager.
Get 152 MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 questions Access in less then $0.12 per day.
MuleSoft Bundle 1:
1 Month PDF Access For All MuleSoft Exams with Updates
$200
$800
Buy Bundle 1
MuleSoft Bundle 2:
3 Months PDF Access For All MuleSoft Exams with Updates
$300
$1200
Buy Bundle 2
MuleSoft Bundle 3:
6 Months PDF Access For All MuleSoft Exams with Updates
$450
$1800
Buy Bundle 3
MuleSoft Bundle 4:
12 Months PDF Access For All MuleSoft Exams with Updates
$600
$2400
Buy Bundle 4
Disclaimer: Fair Usage Policy - Daily 5 Downloads
MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 Test Dumps
Exam Code: MCPA-LEVEL-1
Exam Name: MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1
- 90 Days Free Updates
- MuleSoft Experts Verified Answers
- Printable PDF File Format
- MCPA-LEVEL-1 Exam Passing Assurance
Get 100% Real MCPA-LEVEL-1 Exam Dumps With Verified Answers As Seen in the Real Exam. MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 Exam Questions are Updated Frequently and Reviewed by Industry TOP Experts for Passing MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect Exam Quickly and Hassle Free.
MuleSoft MCPA-LEVEL-1 Test Dumps
Struggling with MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 preparation? Get the edge you need! Our carefully created MCPA-LEVEL-1 test dumps give you the confidence to pass the exam. We offer:
1. Up-to-date MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect practice questions: Stay current with the latest exam content.
2. PDF and test engine formats: Choose the study tools that work best for you.
3. Realistic MuleSoft MCPA-LEVEL-1 practice exam: Simulate the real exam experience and boost your readiness.
Pass your MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect exam with ease. Try our study materials today!
Prepare your MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect exam with confidence!We provide top-quality MCPA-LEVEL-1 exam dumps materials that are:
1. Accurate and up-to-date: Reflect the latest MuleSoft exam changes and ensure you are studying the right content.
2. Comprehensive Cover all exam topics so you do not need to rely on multiple sources.
3. Convenient formats: Choose between PDF files and online MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 practice questions for easy studying on any device.
Do not waste time on unreliable MCPA-LEVEL-1 practice test. Choose our proven MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect study materials and pass with flying colors. Try Dumps4free MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 2024 material today!
-
Assurance
MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 practice exam has been updated to reflect the most recent questions from the MuleSoft MCPA-LEVEL-1 Exam.
-
Demo
Try before you buy! Get a free demo of our MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect exam dumps and see the quality for yourself. Need help? Chat with our support team.
-
Validity
Our MuleSoft MCPA-LEVEL-1 PDF contains expert-verified questions and answers, ensuring you're studying the most accurate and relevant material.
-
Success
Achieve MCPA-LEVEL-1 success! Our MuleSoft Certified Platform Architect - Level 1 exam questions give you the preparation edge.
If you have any question then contact our customer support at live chat or email us at support@dumps4free.com.
|

