
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Search heads in a company's European offices need to be able to search data in their New York offices. They also need to restrict access to certain indexers. What should be configured to allow this type of action?
A. Indexer clustering
B. LDAP control
C. Distributed search
D. Search head clustering
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. Distributed search is the feature that allows search heads in a
company’s European offices to search data in their New York offices.Distributed search
also enables restricting access to certain indexers by using the splunk_server field or the
server.conf file1.
Distributed search is a way to scale your Splunk deployment by separating the search
management and presentation layer from the indexing and search retrieval layer. With
distributed search, a Splunk instance called a search head sends search requests to a
group of indexers, or search peers, which perform the actual searches on their indexes.The
search head then merges the results back to the user2.
Distributed search has several use cases, such as horizontal scaling, access control, and
managing geo-dispersed data.For example, users in different offices can search data
across the enterprise or only in their local area, depending on their needs and
permissions2.
The other options are incorrect because:
A. Indexer clustering is a feature that replicates data across a group of indexers to
ensure data availability and recovery.Indexer clustering does not directly affect
distributed search, although search heads can be configured to search across an
indexer cluster3.
B. LDAP control is a feature that allows Splunk to integrate with an external LDAP
directory service for user authentication and role mapping. LDAP control does not
affect distributed search, although it can be used to manage user access to data
and searches.
D. Search head clustering is a feature that distributes the search workload across
a group of search heads that share resources, configurations, and jobs. Search
head clustering does not affect distributed search, although the search heads in a
cluster can search across the same set of indexers.
This file has been manually created on a universal forwarder
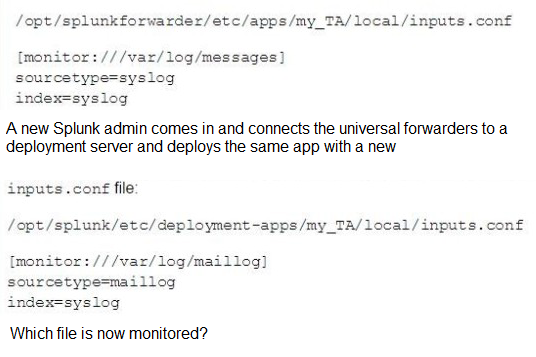
A. /var/log/messages
B. /var/log/maillog
C. /var/log/maillog and /var/log/messages
D. none of the above
An add-on has configured field aliases for source IP address and destination IP address fields. A specific user prefers not to have those fields present in their user context. Based on the defaultprops.confbelow, whichSPLUNK_HOME/etc/users/buttercup/myTA/local/props.confstanza can be added to the user’s local context to disable the field aliases?
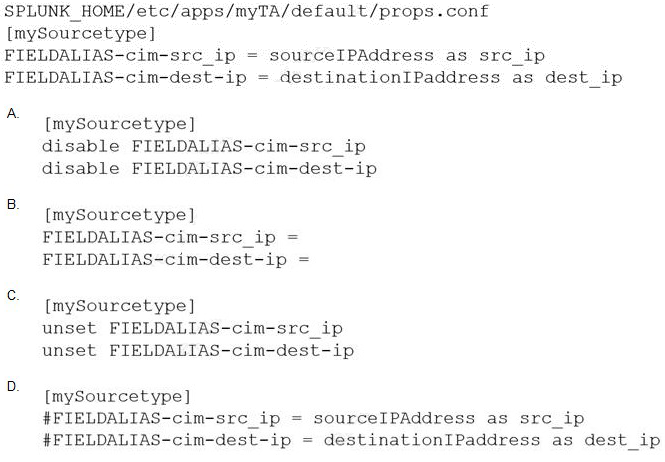
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
The following stanza is active in indexes.conf:
[cat_facts]
maxHotSpanSecs = 3600
frozenTimePeriodInSecs = 2630000
maxTota1DataSizeMB = 650000
All other related indexes.conf settings are default values.
If the event timestamp was 3739283 seconds ago, will it be searchable?
A. Yes, only if the bucket is still hot.
B. No, because the index will have exceeded its maximum size.
C. Yes, only if the index size is also below 650000 MB.
D. No, because the event time is greater than the retention time.
Explanation: The correct answer is D. No, because the event time is greater than the
retention time.
According to the Splunk documentation1, the frozenTimePeriodInSecs setting in
indexes.conf determines how long Splunk software retains indexed data before deleting it
or archiving it to a remote storage. The default value is 188697600 seconds, which is
equivalent to six years. The setting can be overridden on a per-index basis.
In this case, the cat_facts index has a frozenTimePeriodInSecs setting of 2630000
seconds, which is equivalent to about 30 days. This means that any event that is older than
30 days from the current time will be removed from the index and will not be searchable.
The event timestamp was 3739283 seconds ago, which is equivalent to about 43 days.
This means that the event is older than the retention time of the cat_facts index and will not
be searchable.
The other settings in the stanza, such as maxHotSpanSecs and maxTota1DataSizeMB, do
not affect the retention time of the events. They only affect the size and duration of the
buckets that store the events.
What is required when adding a native user to Splunk? (select all that apply)
A. Password
B. Username
C. Full Name
D. Default app
Explanation: According to the Splunk system admin course PDF, When adding native users, Username and Password ARE REQUIRED
| Page 8 out of 37 Pages |
| Previous |