
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 2: Questions Set 2
This is what Splunk uses to categorize the data that is being indexed
A. Host
B. Sourcetype
C. Index
D. Source
Consider the following search:
Index=web sourcetype=access_combined
The log shows several events that share the same JSESSIONID value
(SD404K289O2F151). View the events as a group. From the following list, which search
groups events by JSESSIONID?
A. index=web sourcetype=access_combined SD404K289O2F151 I table JSESSIONID
B. index=web sourcetype=access_combined JSESSIONID
C. index=web sourcetype=access_combined I highlight JSESSIONID I search SD404K289O2F151
D. index-web sourcetype=access_combined I transaction JSESSIONID I search SD404K289O2F151
Which of the following objects can a calculated field use as a source?
A. An alias of a field.
B. A field added by an automatic lookup.
C. The tag field.
D. The eventtype field.
Explanation: The correct answer is B. A field added by an automatic lookup.
A calculated field is a field that is added to events at search time by using an eval
expression. A calculated field can use the values of two or more fields that are already present in the events to perform calculations.A calculated field can use any field as a
source, as long as the field is extracted before the calculated field is defined1.
An automatic lookup is a way to enrich events with additional fields from an external
source, such as a CSV file or a database.An automatic lookup can add fields to
eventsbased on the values ofexisting fields, such as host, source, sourcetype, or any other
extracted field2.An automatic lookup is performed before the calculated fields are defined,
so the fields added by the lookup can be used as sources for the calculated fields3.
Therefore, a calculated field can use a field added by an automatic lookup as a source.
Which of the following is included with the Common Information Model (CIM) add-on?
A. Search macros
B. Event category tags
C. Workflow actions
D. tsidx files
Explanation: The correct answer is B. Event category tags. This is because the CIM addon contains a collection of preconfigured data models that you can apply to your data at search time. Each data model in the CIM consists of a set of field names and tags that define the least common denominator of a domain of interest. Event category tags are used to classify events into high-level categories, such as authentication, network traffic, or web activity. You can use these tags to filter and analyze events based on their category. You can learn more about event category tags from the Splunk documentation12. The other options are incorrect because they are not included with the CIM add-on. Search macros are reusable pieces of search syntax that you can invoke from other searches. They are not specific to the CIM add-on, although some Splunk apps may provide their own search macros. Workflow actions are custom links or scripts that you can run on specific fields or events. They are also not specific to the CIM add-on, although some Splunk apps may provide their own workflow actions. tsidx files are index files that store the terms and pointers to the raw data in Splunk buckets. They are part of the Splunk indexing process and have nothing to do with the CIM add-on.
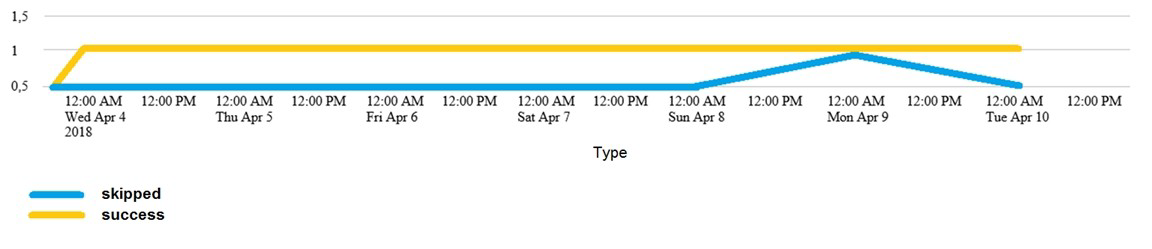
Which of the following searches would create a graph similar to the one below?
A. index_internal seourcetype=Savesplunker | fields sourcetype, status | transaction status maxspan-id | start count states
B. index_internal seourcetype=Savesplunker | fields sourcetype, status | transaction status maxspan-id | chart count states by -time
C. index_internal seourcetype=Savesplunker | fields sourcetype, status | transaction status maxspan-id | timechart count by status
D. None of these searches would generate a similart graph.
Explanation: The following search would create a graph similar to the one below:
index_internal sourcetype=Savesplunker | fields sourcetype, status | transaction status
maxspan=1d | timechart count by status
The search does the following:
It uses index_internal to specify the internal index that contains Splunk logs and
metrics.
It uses sourcetype=Savesplunker to filter events by the sourcetype that indicates
the Splunk Enterprise Security app.
It uses fields sourcetype, status to keep only the sourcetype and status fields in
the events.
It uses transaction status maxspan=1d to group events into transactions based on
the status field with a maximum time span of one day between the first and last
events in a transaction.
It uses timechart count by status to create a time-based chart that shows the count
of transactions for each status value over time.
The graph shows the following:
It is a line graph with two lines, one yellow and one blue.
The x-axis is labeled with dates from Wed, Apr 4, 2018 to Tue, Apr 10, 2018.
The y-axis is labeled with numbers from 0 to 15.
The yellow line represents “shipped” and the blue line represents “success”.
The yellow line has a steady increase from 0 to 15, while the blue line has a sharp
increase from 0 to 5, then a decrease to 0, and then a sharp increase to 10.
The graph is titled “Type”.
| Page 4 out of 55 Pages |
| Previous |