
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 2: Misc. Questions
You are deploying a microservices application to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) that will
broadcast livestreams. You expect unpredictable traffic patterns and large variations in the
number of concurrent users. Your application must meet the following requirements:
A. Distribute your workload evenly using a multi-zonal node pool.
B. Distribute your workload evenly using multiple zonal node pools.
C. Use cluster autoscaler to resize the number of nodes in the node pool, and use a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler to scale the workload.
D. Create a managed instance group for Compute Engine with the cluster nodes. Configure autoscaling rules for the managed instance group.
E. Create alerting policies in Cloud Monitoring based on GKE CPU and memory utilization. Ask an on-duty engineer to scale the workload by executing a script when CPU and memory usage exceed predefined thresholds.
Your application is controlled by a managed instance group. You want to share a large read-only data set between all the instances in the managed instance group. You want to ensure that each instance can start quickly and can access the data set via its filesystem with very low latency. You also want to minimize the total cost of the solution. What should you do?
A. Move the data to a Cloud Storage bucket, and mount the bucket on the filesystem using Cloud Storage FUSE.
B. Move the data to a Cloud Storage bucket, and copy the data to the boot disk of the instance via a startup script.
C. Move the data to a Compute Engine persistent disk, and attach the disk in read-only mode to multiple Compute Engine virtual machine instances.
D. Move the data to a Compute Engine persistent disk, take a snapshot, create multiple disks from the snapshot, and attach each disk to its own instance.
Your organization has recently begun an initiative to replatform their legacy applications onto Google Kubernetes Engine. You need to decompose a monolithic application into microservices. Multiple instances have read and write access to a configuration file, which is stored on a shared file system. You want to minimize the effort required to manage this transition, and you want to avoid rewriting the application code. What should you do?
A. Create a new Cloud Storage bucket, and mount it via FUSE in the container.
B. Create a new persistent disk, and mount the volume as a shared PersistentVolume.
C. Create a new Filestore instance, and mount the volume as an NFS PersistentVolume.
D. Create a new ConfigMap and volumeMount to store the contents of the configuration file.
ConfigMaps bind non-sensitive configuration artifacts such as configuration files,
command-line arguments, and environment variables to your Pod containers and system
components at runtime.
A ConfigMap separates your configurations from your Pod and components, which helps
keep your workloads portable. This makes their configurations easier to change and
manage, and prevents hardcoding configuration data to Pod specifications.
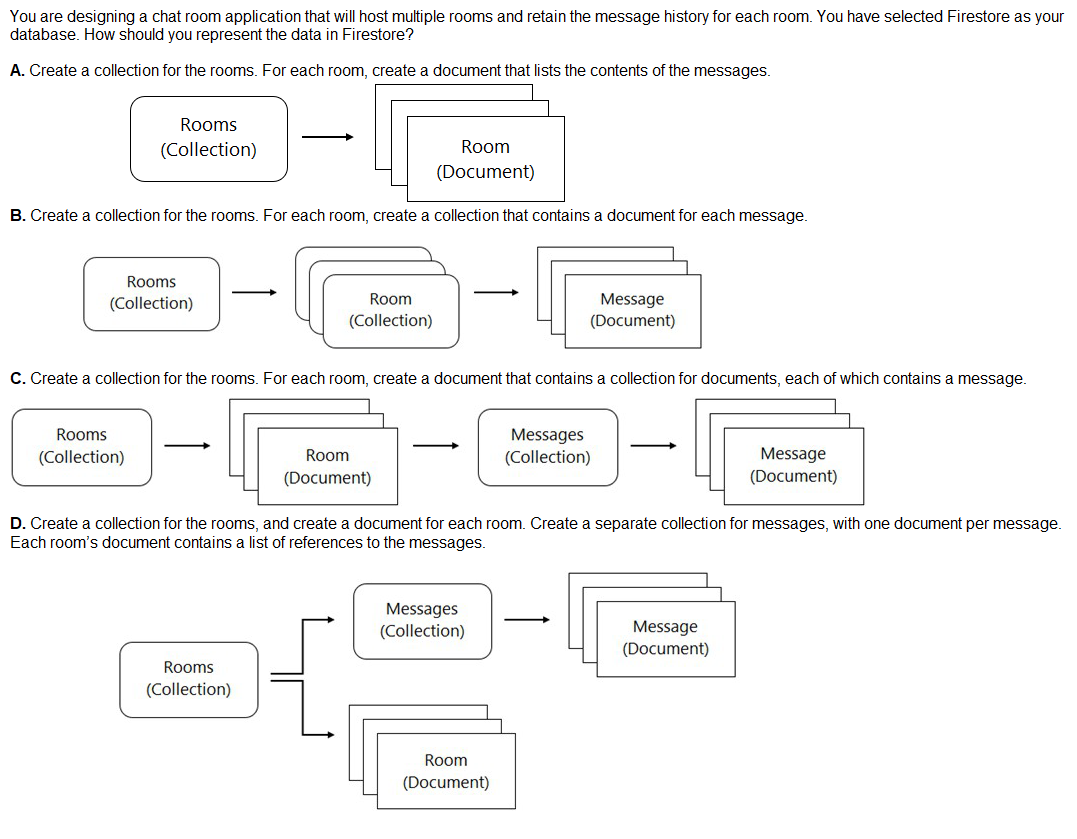
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
You are running a web application on Google Kubernetes Engine that you inherited. You want to determine whether the application is using libraries with known vulnerabilities or is vulnerable to XSS attacks. Which service should you use?
A. Google Cloud Armor
B. Debugger
C. Web Security Scanner
D. Error Reporting
Web Security Scanner identifies security vulnerabilities in your App Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and Compute Engine web applications. It crawls your application, following all links within the scope of your starting URLs, and attempts to exercise as many user inputs and event handlers as possible.
| Page 7 out of 51 Pages |
| Previous |