Question # 1
| A security engineer wants to upgrade the company's deployed firewalls from PAN-OS 10.1
to 11.0.x to take advantage of the new TLSvl.3 support for management access.
What is the recommended upgrade path procedure from PAN-OS 10.1 to 11.0.x? |
A. Required: Download PAN-OS 10.2.0 or earlier release that is not EOL.
Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.2 maintenance release and
reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 11.0.0. Required: Download and install the desired
PAN-OS 11.0.x. | B. Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.1 maintenance release
and reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 10.2.0.
Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.2 maintenance release and
reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 11.0.0.
Required: Download and install the desired
PAN-OS 11.0.x. | C. Optional: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.1 release.
Optional:
Install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.2 maintenance release.
Required: Download PANOS
11.0.0.
Required: Download and install the desired PAN-OS 11.0.x. | D. Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.1 maintenance release
and reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 10.2.0.
Optional: Install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.2 maintenance release.
Required:
Download PAN-OS 11.0.0.
Required: Download and install the desired PAN-OS 11.0.x. |
B. Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.1 maintenance release
and reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 10.2.0.
Required: Download and install the latest preferred PAN-OS 10.2 maintenance release and
reboot.
Required: Download PAN-OS 11.0.0.
Required: Download and install the desired
PAN-OS 11.0.x.
Explanation: Palo Alto Networks recommends following a specific upgrade path when
upgrading PAN-OS to ensure compatibility and minimize the risk of issues. The
recommended path involves sequential upgrades through major releases.
B. The detailed upgrade path from PAN-OS 10.1 to 11.0.x involves:
First, upgrading to the latest preferred maintenance release of the current PAN-OS
version (10.1) to ensure that all the latest fixes and improvements are applied.
Next, upgrading to the base version of the next major release (PAN-OS 10.2.0),
followed by upgrading to the latest preferred maintenance release of PAN-OS
10.2. This step ensures that the firewall is on a stable and supported version
before proceeding to the next major release.
Finally, upgrading to the base version of PAN-OS 11.0 (11.0.0), followed by the
desired PAN-OS 11.0.x version. This step completes the upgrade to the new major
version, providing access to new features and improvements, such as TLSv1.3
support for management access.
This sequential upgrade path is designed to ensure a smooth transition between major
versions, maintaining system stability and security.
Question # 2
| A company wants to add threat prevention to the network without redesigning the network
routing.
What are two best practice deployment modes for the firewall? (Choose two.) |
| A. VirtualWire | | B. Layer3 | | C. TAP | | D. Layer2 |
A. VirtualWire
D. Layer2
Explanation:
A and D are the best practice deployment modes for the firewall if the company
wants to add threat prevention to the network without redesigning the network
routing. This is because these modes allow the firewall to act as a transparent
device that does not affect the existing network topology or routing1.
A: VirtualWire mode allows the firewall to be inserted into any existing network
segment without changing the IP addressing or routing of that segment2. The
firewall inspects traffic between two interfaces that are configured as a pair, called
a virtual wire. The firewall applies security policies to the traffic and forwards it to
the same interface from which it was received2.
D: Layer 2 mode allows the firewall to act as a switch that forwards traffic based on
MAC addresses3. The firewall inspects traffic between interfaces that are
configured as Layer 2 interfaces and belong to the same VLAN. The firewall
applies security policies to the traffic and forwards it to the appropriate interface
based on the MAC address table3.
Question # 3
An engineer is reviewing the following high availability (HA) settings to understand a recent
HAfailover event.
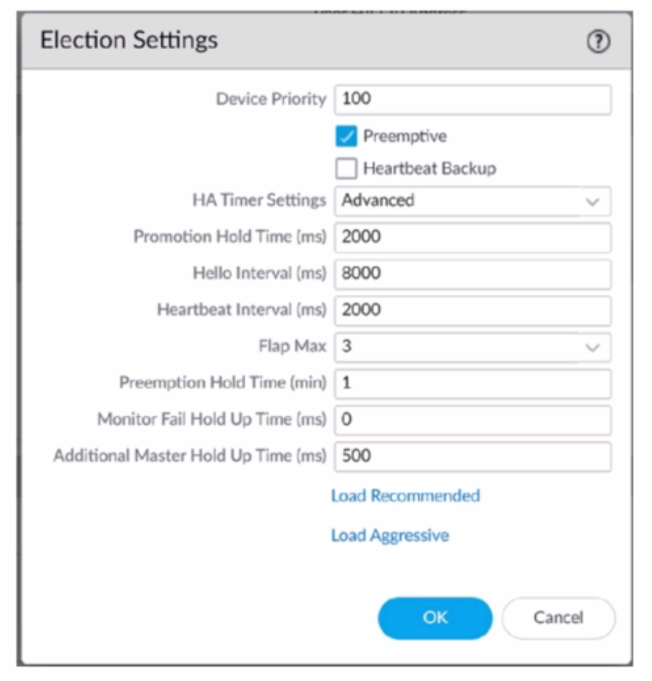
Which timer determines the frequency between packets sent to verify that the HA
functionality on the other HA firewall is operational? |
| A. Monitor Fail Hold Up Time
| | B. Promotion Hold Time
| | C. Heartbeat Interval
| | D. Hello Interval |
D. Hello Interval
The timer that determines the frequency between packets sent to verify that the HA
functionality on the other HA firewall is operational is the Hello Interval. The Hello Interval is
the interval in milliseconds between hello packets that are sent to check the HA status of
the peer firewall. The default value for the Hello Interval is 8000 ms for all platforms, and
the range is 8000-60000 ms. If the firewall does not receive a hello packet from its peer
within the specified interval, it will declare the peer as failed and initiate a
failover12.
Question # 4
| An engineer configures a specific service route in an environment with multiple virtual
systems instead of using the inherited global service route configuration.
What type of service route can be used for this configuration? |
| A. IPv6 Source or Destination Address
| | B. Destination-Based Service Route
| | C. IPv4 Source Interface
| | D. Inherit Global Setting |
C. IPv4 Source Interface
Question # 5
| Which three statements accurately describe Decryption Mirror? (Choose three.) |
| A. Decryption Mirror requires a tap interface on the firewall
| | B. Use of Decryption Mirror might enable malicious users with administrative access to the
firewall to harvest sensitive information that is submitted via an encrypted channel
| | C. Only management consent is required to use the Decryption Mirror feature.
| | D. Decryption, storage, inspection, and use of SSL traffic are regulated in certain countries.
| | E. You should consult with your corporate counsel before activating and using Decryption
Mirror in a production environment. |
B. Use of Decryption Mirror might enable malicious users with administrative access to the
firewall to harvest sensitive information that is submitted via an encrypted channel
D. Decryption, storage, inspection, and use of SSL traffic are regulated in certain countries.
E. You should consult with your corporate counsel before activating and using Decryption
Mirror in a production environment.
Explanation: Decryption Mirror is a feature that allows a Palo Alto Networks firewall to
send a copy of decrypted traffic to an external security device or tool for further analysis.
The potential risk associated with Decryption Mirror is that if the firewall administrator's
credentials are compromised, a malicious user could potentially access sensitive decrypted
information. Hence, it's advised to be cautious and ensure proper handling of this feature.
Additionally, laws and regulations regarding the decryption, storage, inspection, and use of
SSL/TLS encrypted traffic vary by country and industry. It is crucial to ensure compliance
with relevant laws and best practices when using Decryption Mirror. This often requires
consultation with corporate legal counsel to understand the implications and ensure that
the use of such features does not violate privacy laws or regulatory requirements.
The need for administrative consent and the legal implications of using Decryption Mirror
features are outlined in Palo Alto Networks' "PAN-OS® Administrator’s Guide" and best
practice documentation. It is not specifically required to have a tap interface to use
Decryption Mirror, which eliminates option A. Option C is incorrect because it is not just
management consent but legal compliance that needs to be considered.
Question # 6
| During the implementation of SSL Forward Proxy decryption, an administrator imports the
company's Enterprise Root CA and Intermediate CA certificates onto the firewall. The
company's Root and Intermediate CA certificates are also distributed to trusted devices
using Group Policy and GlobalProtect. Additional device certificates and/or Subordinate
certificates requiring an Enterprise CA chain of trust are signed by the company's
Intermediate CA.
Which method should the administrator use when creating Forward Trust and Forward
Untrust certificates on the firewall for use with decryption? |
| A. Generate a single subordinate CA certificate for both Forward Trust and Forward
Untrust.
| | B. Generate a CA certificate for Forward Trust and a self-signed CA for Forward Untrust.
| | C. Generate a single self-signed CA certificate for Forward Trust and another for Forward
Untrust
| | D. Generate two subordinate CA certificates, one for Forward Trust and one for Forward
Untrust. |
B. Generate a CA certificate for Forward Trust and a self-signed CA for Forward Untrust.
Question # 7
| An administrator wants to add User-ID information for their Citrix MetaFrame Presentation
Server (MPS) users.
Which option should the administrator use? |
| A. Terminal Server Agent for User Mapping
| | B. Windows-Based User-ID Agent
| | C. PAN-OS Integrated User-ID Agent
| | D. PAN-OS XML API |
A. Terminal Server Agent for User Mapping
Explanation: If you have clients running multi-user systems in a Windows environment,
such as Microsoft Terminal Server or Citrix Metaframe Presentation Server or XenApp,
Configure the Palo Alto Networks Terminal Server (TS) Agent for User Mapping.
Question # 8
| An administrator is receiving complaints about application performance degradation. After
checking the ACC, the administrator observes that there is an excessive amount of VoIP
traffic.
Which three elements should the administrator configure to address this issue? (Choose
three.) |
| A. An Application Override policy for the SIP traffic
| | B. QoS on the egress interface for the traffic flows
| | C. QoS on the ingress interface for the traffic flows
| | D. A QoS profile defining traffic classes
| | E. A QoS policy for each application ID |
B. QoS on the egress interface for the traffic flows
D. A QoS profile defining traffic classes
E. A QoS policy for each application ID
Explanation: To address the issue of application performance degradation due to
excessive VoIP traffic, the administrator should configure QoS on the egress interface for
the traffic flows and a QoS profile defining traffic classes. QoS stands for Quality of
Service, which is a feature that allows the firewall to manage bandwidth usage and
prioritize traffic based on various criteria, such as application, user, service, etc. QoS can
help improve the performance and quality of latency-sensitive applications, such as VoIP,
by guaranteeing them sufficient bandwidth and priority over other traffic1.
To enable QoS on the firewall, the administrator needs to create a QoS profile and a QoS
policy. A QoS profile defines the eight classes of service that traffic can receive, including
priority, guaranteed bandwidth, maximum bandwidth, and weight. A QoS policy identifies
the traffic that matches a specific class of service based on source and destination zones,
addresses, users, applications, services, etc2. The administrator can also create a custom
QoS profile or use the default one.
The administrator should apply QoS on the egress interface for the traffic flows, which is
the interface where the traffic leaves the firewall. This is because QoS can only shape
outbound traffic and not inbound traffic. The egress interface can be either internal or
external, depending on the direction of the VoIP traffic. For example, if the VoIP traffic is
from internal users to external servers, then the egress interface is the untrust interface
facing the ISP. If the VoIP traffic is from external users to internal servers, then the egress
interface is the trust interface facing the LAN3.
The administrator should assign a high priority and a sufficient guaranteed bandwidth to the
VoIP traffic in the QoS profile. This will ensure that the VoIP packets are processed first by
the firewall and are not dropped or delayed due to congestion. The administrator can also
limit or block other applications that consume too much bandwidth or pose security risks in
the same or different QoS classes4.
An Application Override policy for SIP traffic is not necessary to address this issue. An
Application Override policy is used to change or customize the App-ID of certain traffic
based on port and protocol criteria. This can be useful for optimizing performance or
security for some applications that are difficult to identify or have non-standard behaviors.
However, SIP is a predefined App-ID that identifies Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) traffic,
which is commonly used for VoIP signaling. The firewall can recognize SIP traffic without
an Application Override policy5.
QoS on the ingress interface for the traffic flows is not effective to address this issue. As
mentioned earlier, QoS can only shape outbound traffic and not inbound traffic. Applying
QoS on the ingress interface will not have any impact on how the firewall handles or
prioritizes the incoming packets6.
A QoS policy for each application is not required to address this issue. A QoS policy can
match multiple applications in a single rule by using application filters or application groups.
This can simplify and consolidate the QoS policy configuration and management. The
administrator does not need to create a separate QoS policy for each application unless
there is a specific need to assign different classes of service or parameters to each
application7.
Get 294 Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 questions Access in less then $0.12 per day.
Palo Alto Networks Bundle 1:
1 Month PDF Access For All Palo Alto Networks Exams with Updates
$200
$800
Buy Bundle 1
Palo Alto Networks Bundle 2:
3 Months PDF Access For All Palo Alto Networks Exams with Updates
$300
$1200
Buy Bundle 2
Palo Alto Networks Bundle 3:
6 Months PDF Access For All Palo Alto Networks Exams with Updates
$450
$1800
Buy Bundle 3
Palo Alto Networks Bundle 4:
12 Months PDF Access For All Palo Alto Networks Exams with Updates
$600
$2400
Buy Bundle 4
Disclaimer: Fair Usage Policy - Daily 5 Downloads
Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 Test Dumps
Exam Code: PCNSE
Exam Name: Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2
- 90 Days Free Updates
- Palo Alto Networks Experts Verified Answers
- Printable PDF File Format
- PCNSE Exam Passing Assurance
Get 100% Real PCNSE Exam Dumps With Verified Answers As Seen in the Real Exam. Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 Exam Questions are Updated Frequently and Reviewed by Industry TOP Experts for Passing Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations Exam Quickly and Hassle Free.
Palo Alto Networks PCNSE Test Dumps
Struggling with Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 preparation? Get the edge you need! Our carefully created PCNSE test dumps give you the confidence to pass the exam. We offer:
1. Up-to-date Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations practice questions: Stay current with the latest exam content.
2. PDF and test engine formats: Choose the study tools that work best for you.
3. Realistic Palo Alto Networks PCNSE practice exam: Simulate the real exam experience and boost your readiness.
Pass your Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations exam with ease. Try our study materials today!
PCNSE Practice Test Details
133 Single Choice Questions
43 Multiple Choice Questions
1 Drag Drop Questions
Official Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations exam info is available on Palo Alto Networks website at https://www.paloaltonetworks.co.uk/services/education/palo-alto-networks-certified-network-security-engineer
Prepare your Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations exam with confidence!We provide top-quality PCNSE exam dumps materials that are:
1. Accurate and up-to-date: Reflect the latest Palo Alto Networks exam changes and ensure you are studying the right content.
2. Comprehensive Cover all exam topics so you do not need to rely on multiple sources.
3. Convenient formats: Choose between PDF files and online Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 practice questions for easy studying on any device.
Do not waste time on unreliable PCNSE practice test. Choose our proven Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations study materials and pass with flying colors. Try Dumps4free Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 2024 material today!
-
Assurance
Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 practice exam has been updated to reflect the most recent questions from the Palo Alto Networks PCNSE Exam.
-
Demo
Try before you buy! Get a free demo of our Palo Alto Certifications and Accreditations exam dumps and see the quality for yourself. Need help? Chat with our support team.
-
Validity
Our Palo Alto Networks PCNSE PDF contains expert-verified questions and answers, ensuring you're studying the most accurate and relevant material.
-
Success
Achieve PCNSE success! Our Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE) PAN-OS 10.2 exam questions give you the preparation edge.
If you have any question then contact our customer support at live chat or email us at support@dumps4free.com.
Questions People Ask About PCNSE Exam
PCNSE exam tests your ability to design, deploy, configure, maintain, and troubleshoot Palo Alto Networks firewalls. It covers topics like security policies, NAT, VPNs, troubleshooting techniques, and understanding the Palo Alto Networks security platform architecture.
Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer (PCNSE) exam is indeed challenging, reflecting its status as a high-level certification. It's designed for individuals with deep knowledge and experience in network security, particularly using Palo Alto Networks solutions.
Palo Alto Networks offers practice exams on their Pearson VUE testing platform, mirroring the real PCNSE's format and difficulty. Additionally, Dumps4free online training platform also provide PCNSE practice test in PDF and online test engine as prep course.
Yes, the PCNSE certification can significantly boost your earning potential. Specialized cybersecurity skills are in high demand, and the PCNSE proves your expertise with Palo Alto Networks firewalls. With some experience, PCNSE holders can command competitive salaries in the cybersecurity field.
PCNSE (Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer) stands out in the realm of cybersecurity certifications for its specific focus on Palo Alto Networks' products and solutions. While other certifications like CISSP or CISM offer a broader view of security principles and management.
It's possible, but highly challenging. The PCNSE assumes some foundational networking knowledge and familiarity with firewall concepts. While dedicated studying can bridge the theory gap, hands-on experience with configuring Palo Alto Networks firewalls provides a significant advantage for the exam.
PCNSA (Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Administrator) is the entry-level certification, focusing on basic firewall administration and daily operational tasks. PCNSE (Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer) is advanced, testing your ability to design, implement, and troubleshoot complex Palo Alto Networks security solutions.
Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer (PCNSE) certification is valid for a period of two years from the date of certification. To maintain the certification's validity, professionals are required to renew it.
Average salary for a PCNSE certified professional in the US can range from $90,000 to $150,000 annually.
|

