
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Which source is the most reliable for collecting User-ID user mapping?
A. Syslog Listener
B. Microsoft Exchange
C. Microsoft Active Directory
D. GlobalProtect
Refer to the exhibit.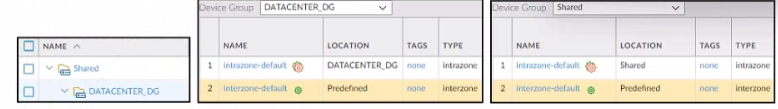
Based on the screenshots above what is the correct order in which the various rules are
deployed to firewalls inside the DATACENTER_DG device group?
A. shared pre-rules
DATACENTER DG pre rules
rules configured locally on the firewall
shared post-rules
DATACENTER_DG post-rules
DATACENTER.DG default rules
B. shared pre-rules
DATACENTER_DG pre-rules
rules configured locally on the firewall
shared post-rules
DATACENTER.DG post-rules
shared default rules
C. shared pre-rules
DATACENTER_DG pre-rules
rules configured locally on the firewall
DATACENTER_DG post-rules
shared post-rules
shared default rules
D. shared pre-rules
DATACENTER_DG pre-rules
rules configured locally on the firewall
DATACENTER_DG post-rules
shared post-rules
DATACENTER_DG default rules
Which three authentication types can be used to authenticate users? (Choose three.)
A. Local database authentication
B. PingID
C. Kerberos single sign-on
D. GlobalProtect client
E. Cloud authentication service
Explanation:
The three authentication types that can be used to authenticate users are:
A: Local database authentication: This is the authentication type that uses the local
user database on the firewall or Panorama to store and verify user credentials1.
C: Cloud authentication service: This is the authentication type that uses a cloudbased
identity provider, such as Okta, PingOne, or PingFederate, to authenticate
users and provide SAML assertions to the firewall or Panorama2.
E: Kerberos single sign-on: This is the authentication type that uses the Kerberos
protocol to authenticate users who are logged in to a Windows domain and provide
them with seamless access to resources on the firewall or Panorama3.
What type of NAT is required to configure transparent proxy?
A. Source translation with Dynamic IP and Port
B. Destination translation with Static IP
C. Source translation with Static IP
D. Destination translation with Dynamic IP
A firewall engineer creates a NAT rule to translate IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10. The engineer also plans to enable DNS rewrite so that the firewall rewrites the IPv4 address in a DNS response based on the original destination IP address and translated destination IP address configured for the rule. The engineer wants the firewall to rewrite a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10. What should the engineer do to complete the configuration?
A. Create a U-Turn NAT to translate the destination IP address 192.168.1.10 to 1.1.1.10 with the destination port equal to UDP/53.
B. Enable DNS rewrite under the destination address translation in the Translated Packet section of the NAT rule with the direction Forward.
C. Enable DNS rewrite under the destination address translation in the Translated Packet section of the NAT rule with the direction Reverse.
D. Create a U-Turn NAT to translate the destination IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10 with the destination port equal to UDP/53.
Explanation: If the DNS response matches the Original Destination Address in the rule, translate the DNS response using the same translation the rule uses. For example, if the rule translates IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10, the firewall rewrites a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10.
| Page 15 out of 59 Pages |
| Previous |