
- Email support@dumps4free.com

You created a VPN community using VPN Manager on FortiManager. You also added gateways to the VPN community. Now you are trying to create firewall policies to permit traffic over the tunnel however, the VPN interfaces do not appear as available options.
A. Create interface mappings for the IPsec VPN interfaces before you use them in a policy.
B. Refresh the device status using the Device Manager so that FortiGate populates the IPSec interfaces
C. Configure the phase 1 settings in the VPN community that you didnt initially configure. FortiGate automatically generates the interfaces after you configure the required settings
D. install the VPN community and gateway configuration on the fortiGate devices so that the VPN interfaces appear on the Policy Objects on fortiManager.
After enabling IPS you receive feedback about traffic being dropped.
What could be the reason?
A. Np-accel-mode is set to enable
B. Traffic-submit is set to disable
C. IPS is configured to monitor
D. Fail-open is set to disable
An administrator has configured two fortiGate devices for an HA cluster. While testing HA failover, the administrator notices that some of the switches in the network continue to send traffic to the former primary device What can the administrator do to fix this problem?
A. Verify that the speed and duplex settings match between me FortiGate interfaces and the connected switch ports
B. Configure set link -failed signal enable under-config system ha on both Cluster members
C. Configure remote Iink monitoring to detect an issue in the forwarding path
D. Configure set send-garp-on-failover enables under config system ha on both cluster members
Refer to the exhibit, which shows two configured FortiGate devices and peering over
FGSP.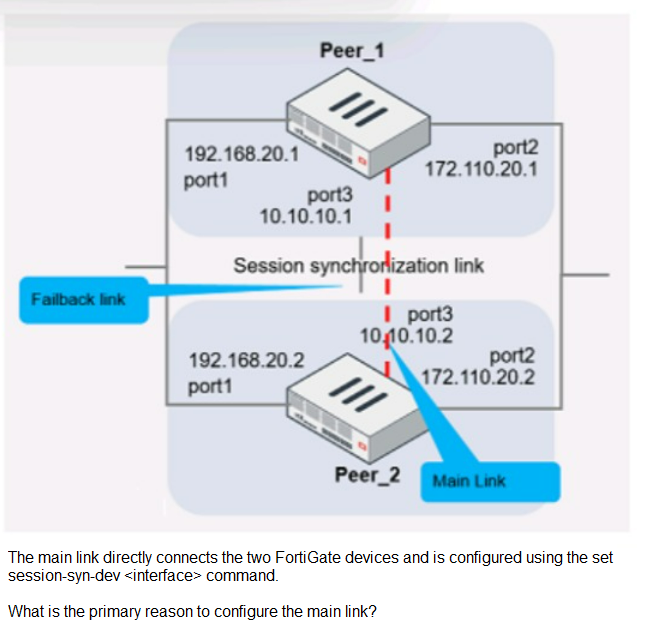
A. To have both sessions and configuration synchronization in layer 2
B. To load balance both sessions and configuration synchronization between layer 2 and 3
C. To have only configuration synchronization in layer 3
D. To have both sessions and configuration synchronization in layer 3
Explanation:
The primary purpose of configuring a main link between the devices is to synchronize
session information so that if one unit fails, the other can continue processing traffic without
dropping active sessions.
A. To have both sessions and configuration synchronization in layer 2.This is incorrect
because FGSP is used for session synchronization, not configuration synchronization.
B. To load balance both sessions and configuration synchronization between layer 2
and 3.FGSP does not perform load balancing and is not used for configuration
synchronization.
C. To have only configuration synchronization in layer 3.The main link is not used
solely for configuration synchronization.
D. To have both sessions and configuration synchronization in layer 3. The main link in
an FGSP setup is indeed used to synchronize session information across the devices, and
it operates at layer 3 since it uses IP addresses to establish the peering.
An administrator is configuring two FortiGate devices in an HA cluster. While configuring
the devices, the administrator issues the following commands on both HA cluster members:
A. They force the former primary to send gratuitous ARP packets when the failover happens to indicate that the virtual MAC address is now using a different device.
B. They force the former primary to shut down all ts interfaces for one second when failover happens, excluding the heartbeat and reserved management interfaces.
C. They force both HA devices for remote link monitoring to detect an issue in the forwarding path.
D. They force the switches to update their MAC forwarding tables, when failover happens.
| Page 4 out of 13 Pages |
| Previous |