
- Email support@dumps4free.com

A company wants to move its Mule API implementations into production as quickly as
possible. To protect access to all Mule application data and metadata, the company
requires that all Mule applications be deployed to the company's customer-hosted
infrastructure within the corporate firewall. What combination of runtime plane and control
plane options meets these project lifecycle goals?
A.
Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and customer-hosted control plane
B.
MuleSoft-hosted runtime plane and customer-hosted control plane
C.
Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and MuleSoft-hosted control plane
D.
iPaaS provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and MuleSoft-hosted control plane
Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and customer-hosted control plane
Explanation:
Explanation
Correct Answer: Manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and customerhosted
control plane
*****************************************
There are two key factors that are to be taken into consideration from the scenario given in
the question.
>> Company requires both data and metadata to be resided within the corporate firewall
>> Company would like to go with customer-hosted infrastructure.
Any deployment model that is to deal with the cloud directly or indirectly (Mulesoft-hosted
or Customer's own cloud like Azure, AWS) will have to share atleast the metadata.
Application data can be controlled inside firewall by having Mule Runtimes on customer
hosted runtime plane. But if we go with Mulsoft-hosted/ Cloud-based control plane, the
control plane required atleast some minimum level of metadata to be sent outside the
corporate firewall.
As the customer requirement is pretty clear about the data and metadata both to be within
the corporate firewall, even though customer wants to move to production as quickly as
possible, unfortunately due to the nature of their security requirements, they have no other
option but to go with manually provisioned customer-hosted runtime plane and customerhosted
control plane.
What is a best practice when building System APIs?
A.
Document the API using an easily consumable asset like a RAML definition
B.
Model all API resources and methods to closely mimic the operations of the backend system
C.
Build an Enterprise Data Model (Canonical Data Model) for each backend system and apply it to System APIs
D.
Expose to API clients all technical details of the API implementation's interaction wifch
the backend system
Model all API resources and methods to closely mimic the operations of the backend system
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Model all API resources and methods to closely mimic the operations of
the backend system.
*****************************************
>> There are NO fixed and straight best practices while opting data models for APIs. They
are completly contextual and depends on number of factors. Based upon those factors, an
enterprise can choose if they have to go with Enterprise Canonical Data Model or Bounded
Context Model etc.
>> One should NEVER expose the technical details of API implementation to their API
clients. Only the API interface/ RAML is exposed to API clients.
>> It is true that the RAML definitions of APIs should be as detailed as possible and should
reflect most of the documentation. However, just that is NOT enough to call your API as
best documented API. There should be even more documentation on Anypoint Exchange
with API Notebooks etc. to make and create a developer friendly API and repository..
>> The best practice always when creating System APIs is to create their API interfaces by
modeling their resources and methods to closely reflect the operations and functionalities
of that backend system.
An organization uses various cloud-based SaaS systems and multiple on-premises
systems. The on-premises systems are an important part of the organization's application
network and can only be accessed from within the organization's intranet.
What is the best way to configure and use Anypoint Platform to support integrations with
both the cloud-based SaaS systems and on-premises systems?
A) Use CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes in an Anypoint VPC managed by Anypoint
Platform Private Cloud Edition control plane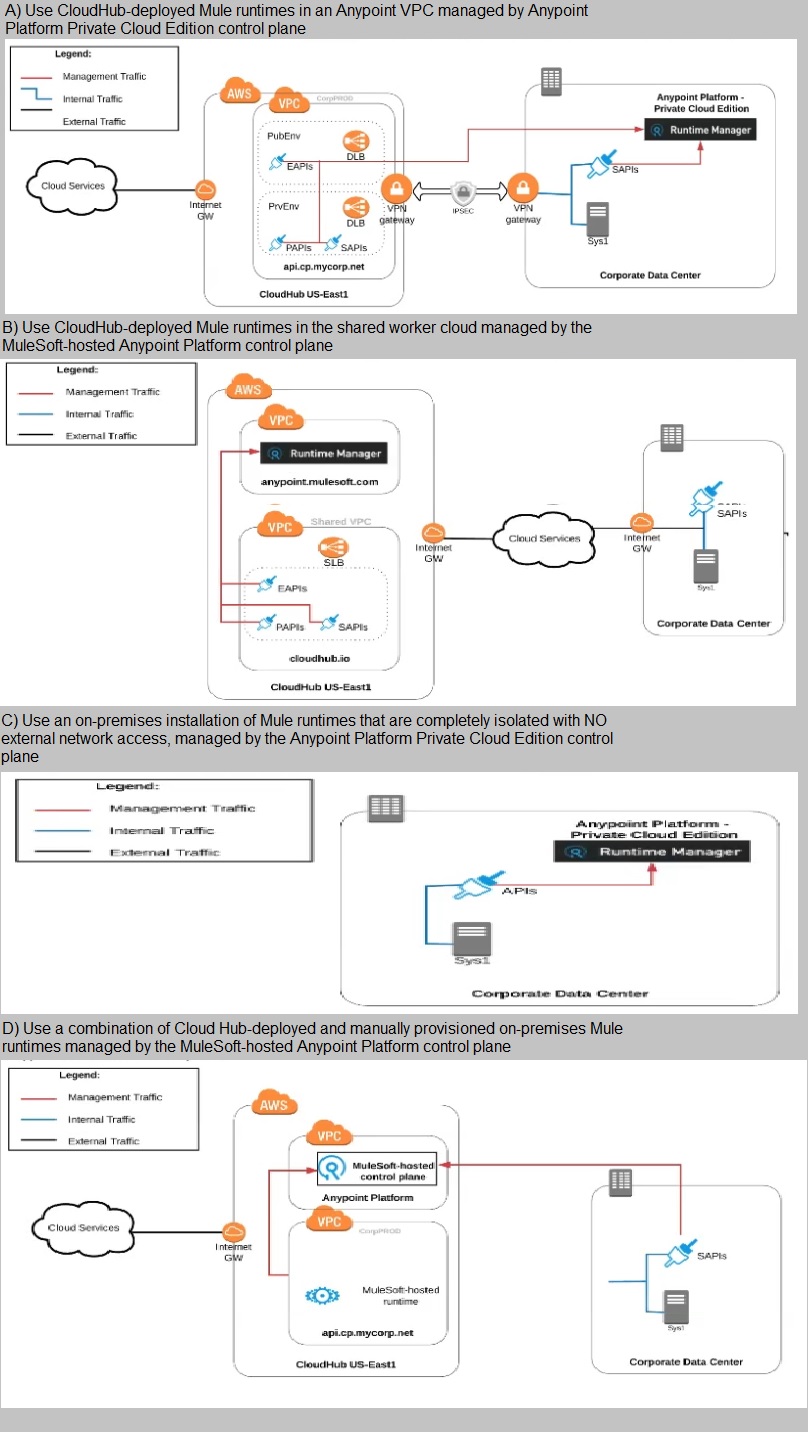
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option B
Explanation: •Explanation
Correct Answer: Use a combination of CloudHub-deployed and manually provisioned onpremises
Mule runtimes managed by the MuleSoft-hosted Platform control plane.
*****************************************
Key details to be taken from the given scenario:
>> Organization uses BOTH cloud-based and on-premises systems
>> On-premises systems can only be accessed from within the organization's intranet
Let us evaluate the given choices based on above key details:
>> CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes can ONLY be controlled using MuleSoft-hosted
control plane. We CANNOT use Private Cloud Edition's control plane to control CloudHub
Mule Runtimes. So, option suggesting this is INVALID
>> Using CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes in the shared worker cloud managed by the
MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform is completely IRRELEVANT to given scenario and silly
choice. So, option suggesting this is INVALID
>> Using an on-premises installation of Mule runtimes that are completely isolated with NO
external network access, managed by the Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition control
plane would work for On-premises integrations. However, with NO external access,
integrations cannot be done to SaaS-based apps. Moreover CloudHub-hosted apps are
best-fit for integrating with SaaS-based applications. So, option suggesting this is BEST
WAY.
The best way to configure and use Anypoint Platform to support these mixed/hybrid
integrations is to use a combination of CloudHub-deployed and manually provisioned onpremises
Mule runtimes managed by the MuleSoft-hosted Platform control plane.
An organization has implemented a Customer Address API to retrieve customer address
information. This API has been deployed to multiple environments and has been configured
to enforce client IDs everywhere.
A developer is writing a client application to allow a user to update their address. The
developer has found the Customer Address API in Anypoint Exchange and wants to use it
in their client application.
What step of gaining access to the API can be performed automatically by Anypoint
Platform?
A.
Approve the client application request for the chosen SLA tier
B.
Request access to the appropriate API Instances deployed to multiple environments using the client application's credentials
C.
Modify the client application to call the API using the client application's credentials
D.
Create a new application in Anypoint Exchange for requesting access to the API
Approve the client application request for the chosen SLA tier
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Approve the client application request for the chosen SLA tier
*****************************************
>> Only approving the client application request for the chosen SLA tier can be automated
>> Rest of the provided options are not valid
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/defining-sla-tiers#defining-a-tier
What is a key requirement when using an external Identity Provider for Client Management in Anypoint Platform?
A.
Single sign-on is required to sign in to Anypoint Platform
B.
The application network must include System APIs that interact with the Identity
Provider
C.
To invoke OAuth 2.0-protected APIs managed by Anypoint Platform, API clients must submit access tokens issued by that same Identity Provider
D.
APIs managed by Anypoint Platform must be protected by SAML 2.0 policies
To invoke OAuth 2.0-protected APIs managed by Anypoint Platform, API clients must submit access tokens issued by that same Identity Provider
Explanation: https://www.folkstalk.com/2019/11/mulesoft-integration-and-platform.html
Explanation
Correct Answer: To invoke OAuth 2.0-protected APIs managed by Anypoint Platform, API
clients must submit access tokens issued by that same Identity Provider
*****************************************
>> It is NOT necessary that single sign-on is required to sign in to Anypoint Platform
because we are using an external Identity Provider for Client Management
>> It is NOT necessary that all APIs managed by Anypoint Platform must be protected by
SAML 2.0 policies because we are using an external Identity Provider for Client
Management
>> Not TRUE that the application network must include System APIs that interact with the
Identity Provider because we are using an external Identity Provider for Client Management
Only TRUE statement in the given options is - "To invoke OAuth 2.0-protected APIs
managed by Anypoint Platform, API clients must submit access tokens issued by that same
Identity Provider"
References:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/external-oauth-2.0-token-validation-policy
https://blogs.mulesoft.com/dev/api-dev/api-security-ways-to-authenticate-and-authorize/
| Page 1 out of 19 Pages |