
- Email support@dumps4free.com

What is required to setup the HTTP Event Collector (HEC)?
A. Each HEC input requires a unique name but token values can be shared.
B. Each HEC input requires an existing forwarder output group.
C. Each HEC input entry must contain a valid token.
D. Each HEC input requires a Source name field.
Consider the scenario where the /var/log directory contains the files secure, messages,
cron, audit. A customer has created the following inputs.conf stanzas in the same Splunk
app in order to attempt to monitor the files secure and messages:
Which file(s) will actually be actively monitored?
A. /var/log/secure
B. /var/log/messages
C. /var/log/messages, /var/log/cron, /var/log/audit, /var/log/secure
D. /var/log/secure, /var/log/messages
As a best practice which of the following should be used to ingest data on clustered indexers?
A. Monitoring (via a process), collecting data (modular inputs) from remote systems/applications
B. Modular inputs, HTTP Event Collector (HEC), inputs.conf monitor stanza
C. Actively listening on ports, monitoring (via a process), collecting data from remote systems/applications
D. splunktcp, splunktcp-ssl, HTTP Event Collector (HEC)
A customer has written the following search:
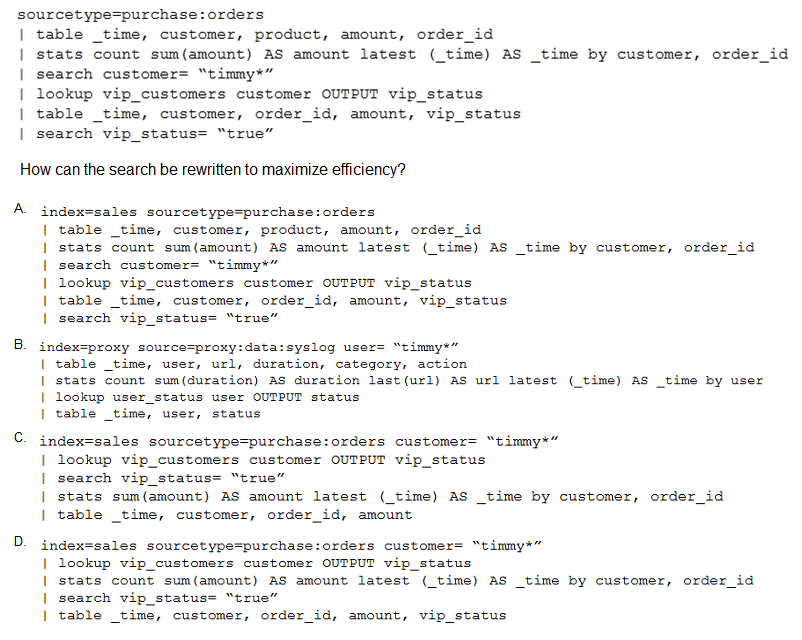
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
When monitoring and forwarding events collected from a file containing unstructured textual events, what is the difference in the Splunk2Splunk payload traffic sent between a universal forwarder (UF) and indexer compared to the Splunk2Splunk payload sent between a heavy forwarder (HF) and the indexer layer? (Assume that the file is being monitored locally on the forwarder.)
A. The payload format sent from the UF versus the HF is exactly the same. The payload size is identical because they’re both sending 64K chunks.
B. The UF sends a stream of data containing one set of medata fields to represent the entire stream, whereas the HF sends individual events, each with their own metadata fields attached, resulting in a lager payload.
C. The UF will generally send the payload in the same format, but only when the sourcetype is specified in the inputs.conf and EVENT_BREAKER_ENABLE is set to true.
D. The HF sends a stream of 64K TCP chunks with one set of metadata fields attached to represent the entire stream, whereas the UF sends individual events, each with their own metadata fields attached.
| Page 5 out of 17 Pages |
| Previous |