
- Email support@dumps4free.com

At what point in the indexing pipeline set is SEDCMD applied to data?
A. In the aggregator queue
B. In the parsing queue
C. In the exec pipeline
D. In the typing pipeline
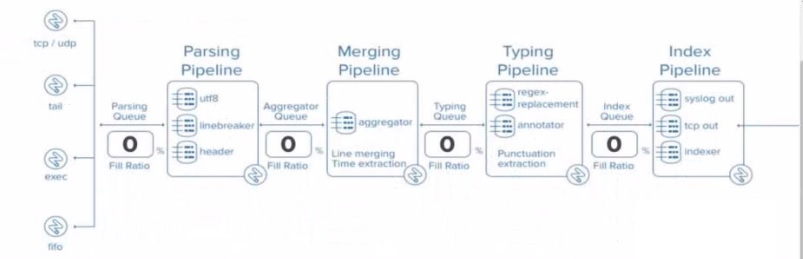
Explanation: In Splunk, SEDCMD (Stream Editing Commands) is applied during the
Typing Pipeline of the data indexing process. The Typing Pipeline is responsible for
various tasks, such as applying regular expressions for field extractions, replacements, and
data transformation operations that occur after the initial parsing and aggregation steps.
Here’s how the indexing process works in more detail:
Parsing Pipeline: In this stage, Splunk breaks incoming data into events, identifies
timestamps, and assigns metadata.
Merging Pipeline: This stage is responsible for merging events and handling timebased
operations.
Typing Pipeline: The Typing Pipeline is where SEDCMD operations occur. It
applies regular expressions and replacements, which is essential for modifying raw
data before indexing. This pipeline is also responsible for field extraction and other
similar operations.
Index Pipeline: Finally, the processed data is indexed and stored, where it
becomes available for searching.
Splunk Cloud Reference: To verify this information, you can refer to the official Splunk
documentation on the data pipeline and indexing process, specifically focusing on the
stages of the indexing pipeline and the roles they play. Splunk Docs often discuss the exact
sequence of operations within the pipeline, highlighting when and where commands like
SEDCMD are applied during data processing.
When should Splunk Cloud Support be contacted?
A. For scripted input troubleshooting.
B. For all configuration changes.
C. When unable to resolve issues or perform problem isolation.
D. For resizing, license changes, or any purchases.
Explanation: Splunk Cloud Support should be contacted when issues arise that cannot be
resolved internally or when problem isolation has been unsuccessful.
C. When unable to resolve issues or perform problem isolation is the correct answer. Splunk Cloud Support is typically involved when internal troubleshooting
has been exhausted, and the issue requires expert assistance or deeper
investigation. While scripted input troubleshooting might be handled by internal
teams, contacting support for unresolved issues is the appropriate step.
When a forwarder phones home to a Deployment Server it compares the check-sum value of the forwarder's app to the Deployment Server's app. What happens to the app If the check-sum values do not match?
A. The app on the forwarder is always deleted and re-downloaded from the Deployment Server.
B. The app on the forwarder is only deleted and re-downloaded from the Deployment Server if the forwarder's app has a smaller check-sum value.
C. The app is downloaded from the Deployment Server and the changes are merged.
D. A warning is generated on the Deployment Server stating the apps are out of sync. An Admin will need to confirm which version of the app should be used.
Explanation: When a forwarder phones home to a Deployment Server, it compares the checksum of its apps with those on the Deployment Server. If the checksums do not match, the app on the forwarder is always deleted and re-downloaded from the Deployment Server. This ensures that the forwarder has the most current and correct version of the app as dictated by the Deployment Server.
When monitoring directories that contain mixed file types, which setting should be omitted from inputs, conf and instead be overridden in propo.conf?
A. sourcetype
B. host
C. source
D. index
Explanation: When monitoring directories containing mixed file types, the sourcetype
should typically be overridden in props.conf rather than defined in inputs.conf. This is
because sourcetype is meant to classify the type of data being ingested, and when dealing
with mixed file types, setting a single sourcetype in inputs.conf would not be effective for
accurate data classification. Instead, you can use props.conf to define rules that apply
different sourcetypes based on the file path, file name patterns, or other criteria. This allows
for more granular and accurate assignment of sourcetypes, ensuring the data is properly
parsed and indexed according to its type.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For further clarification, refer to Splunk's official documentation
on configuring inputs and props, especially the sections discussing monitoring directories
and configuring sourcetypes.
When adding a directory monitor and specifying a sourcetype explicitly, it applies to all files in the directory and subdirectories. If automatic sourcetyping is used, a user can selectively override it in which file on the forwarder?
A. transforms.conf
B. props.conf
C. inputs.conf
D. outputs.cont
Explanation: When a directory monitor is set up with automatic sourcetyping, a user can selectively override the sourcetype assignment by configuring the props.conf file on the forwarder. The props.conf file allows you to define how data should be parsed and processed, including assigning or overriding sourcetypes for specific data inputs.
| Page 5 out of 16 Pages |
| Previous |