
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 1: Part 1
What are the following activities part of?
A. Security Architecture
B. Phase A
C. Phase G
D. Risk Management
Explanation:
Risk management is a generic technique that can be applied across all phases of the Architecture Development Method (ADM), as well as in the Preliminary Phase and the Requirements Management Phase2. Risk management involves the following steps1:
Risk identification: This step involves identifying the potential risks that may affect the architecture project, such as technical, business, organizational, environmental, or legal risks. The risks can be identified through various sources, such as stakeholder interviews, workshops, surveys, checklists, historical data, or expert judgment.
Risk classification: This step involves categorizing the risks based on their nature, source, impact, and priority. The risks can be classified according to different criteria, such as time, cost, scope, quality, security, or compliance. The classification helps in prioritizing the risks and allocating resources and efforts to address them effectively.
Initial risk assessment: This step involves assessing the likelihood and impact of each risk, and determining the initial level of risk. The likelihood is the probability of the risk occurring, and the impact is the severity of the consequences if the risk occurs. The initial level of risk is the product of the likelihood and impact, and it indicates the urgency and importance of the risk. The initial risk assessment helps in identifying the most critical risks that need immediate attention and mitigation.
Refer to the table below: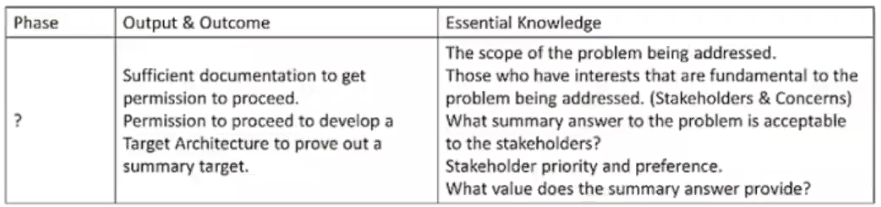
Which ADM Phase does this describe?
A. Phase A
B. Phase B
C. Preliminary Phase
D. Phase C
Explanation: Phase B of the ADM cycle is the Business Architecture phase. It describes the development of a Business Architecture to support an agreed Architecture Vision. The objectives of this phase are to describe the baseline and target Business Architecture, identify candidate Architecture Roadmap components based on gaps between the baseline and target, and determine whether an incremental approach is required.
What is an objective of the ADM Implementation Governance Phase?
A. To provide continual monitoring of the governance framework
B. To ensure conformance for the target architecture
C. To finalize the Implementation and Migration Plan
D. To establish the resources for architecture governance
Explanation: The objective of the ADM Implementation Governance Phase is to provide an architectural oversight of the implementation and to ensure conformance for the target architecture. This phase involves establishing procedures and processes to monitor and control the implementation projects and to verify that they comply with the defined architecture.
Consider the following ADM phases objectives.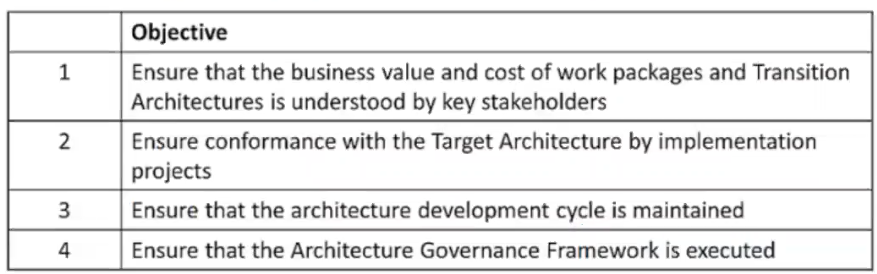
Which phase does each objective match?
A. 1F-2G-3G-4H
B. 1H-2F-3F-4G
C. 1F-2G-3H-4H
D. 1G-2H-3H-4F
According to the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, the ADM phases and their
objectives are as follows1:
Based on the above definitions, we can match each objective with the
corresponding phase as follows:
Which of the following supports the need to govern Enterprise Architecture?
A. The Architecture Project mandates the governance of the target architecture
B. The TOGAF standard cannot be used without executive governance
C. Best practice governance enables the organization to control value realization
D. The Stakeholders preferences may go beyond the architecture project scope and needs control
Explanation: This statement best supports the need to govern Enterprise Architecture. Best practice governance enables the organization to control value realization by ensuring that architectures are aligned with the enterprise’s strategy and objectives, meet the quality and performance requirements, and deliver the expected benefits and outcomes. The Architecture Project does not mandate the governance of the target architecture, but rather follows the governance framework established by the enterprise. The TOGAF standard can be used without executive governance, but it is recommended that executive sponsorship and support are obtained for successful architecture development and transition. The Stakeholders preferences may go beyond the architecture project scope and need control, but this is not the primary reason for governing Enterprise Architecture.
| Page 6 out of 21 Pages |
| Previous |