
- Email support@dumps4free.com

An HA topology is using the following configuration:
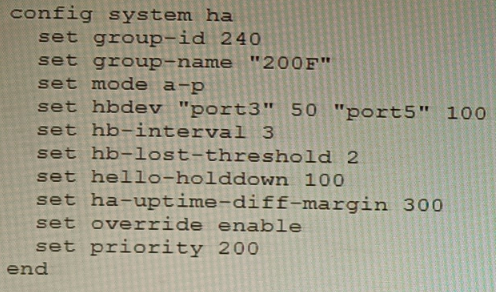
Based on this configuration, how long will it take for a failover to be detected by the
secondary cluster member?
A. 600ms
B. 200ms
C. 300ms
D. 100ms
Explanation: The HA heartbeat interval is 100ms, and the number of lost heartbeats before a failover is detected is 2. So, it will take 2 * 100ms = 200ms for a failover to be detected by the secondary cluster member.
Refer to the exhibits, which show a firewall policy configuration and a network topology.
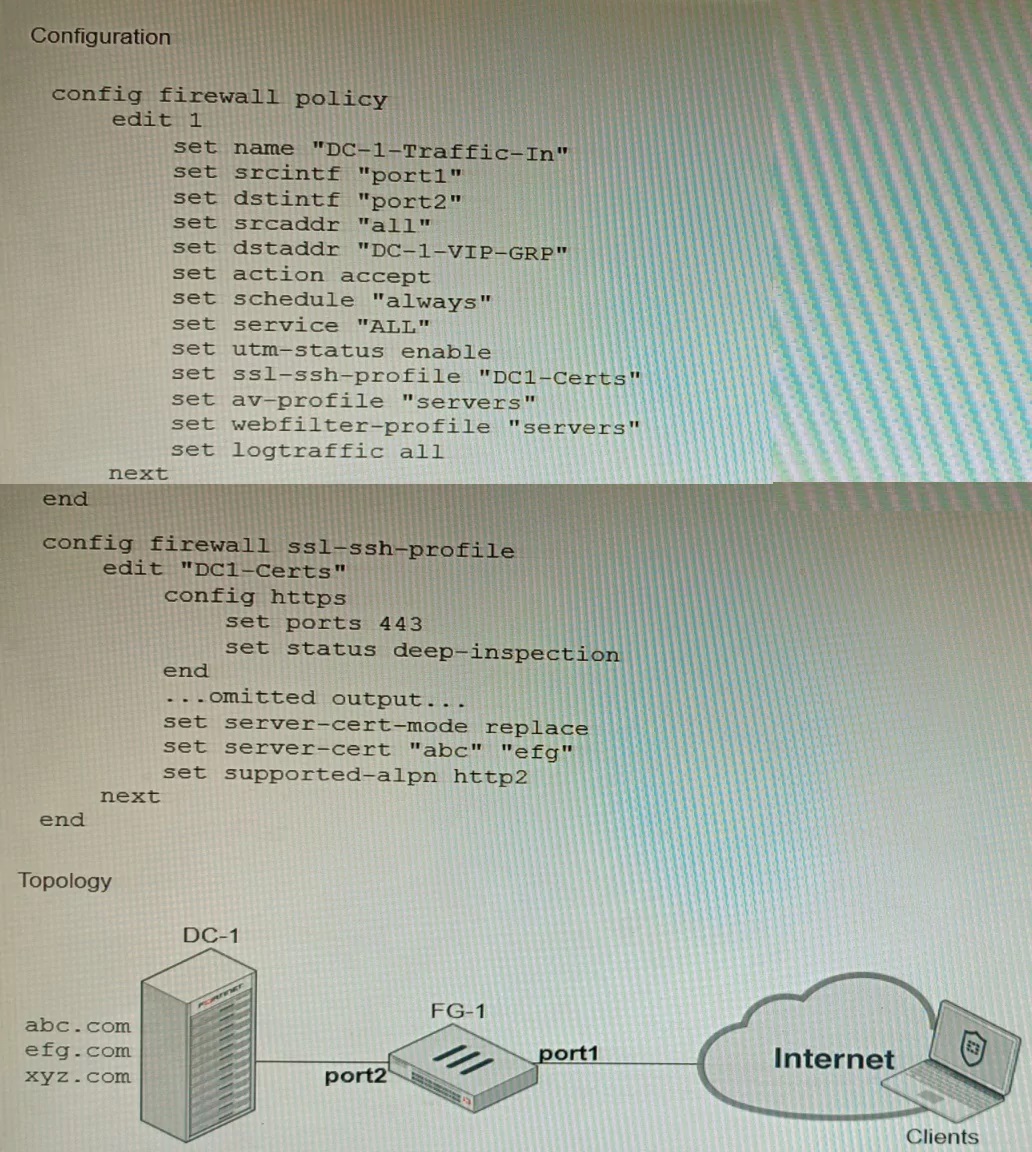
An administrator has configured an inbound SSL inspection profile on a FortiGate device
(FG-1) that is protecting a data center hosting multiple web pages-Given the scenario
shown in the exhibits, which certificate will FortiGate use to handle requests to xyz.com?
A. FortiGate will fall-back to the default Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate.
B. FortiGate will reject the connection since no certificate is defined.
C. FortiGate will use the Fortinet_CA_Untrusted certificate for the untrusted connection,
D. FortiGate will use the first certificate in the server-cert list—the abc.com certificate
Explanation: When using inbound SSL inspection, FortiGate needs to present a certificate to the client that matches the requested domain name. If no matching certificate is found in the server-cert list, FortiGate will fall-back to the default Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate, which is self-signed and may trigger a warning on the client browser.
A. The FortiGate was not configured with the correct pre-shared key to connect to the FortiManager
B. The DHCP server was not configured with the FQDN of the FortiManager
C. The DHCP server used the incorrect option type for the FortiManager IP address.
D. The configuration was modified on the FortiGate prior to connecting to the FortiManager
Explanation: C is correct because the DHCP server used the incorrect option type for the FortiManager IP address. The option type should be 43 instead of 15, as shown in the FortiManager Administration Guide under Zero-Touch Provisioning > Configuring DHCP options for ZTP.
You are troubleshooting a FortiMail Cloud service integrated with Office 365 where outgoing emails are not reaching the recipients' mail What are two possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two.)
A. The FortiMail access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is missing.
B. The FortiMail DKIM key was not set using the Auto Generation option.
C. The FortiMail access control rules to relay from Office 365 servers public IPs are missing.
D. A Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center has not been set properly to the FortiMail Cloud FQDN.
Explanation: A. The FortiMail access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is
missing.
If the access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is missing, then FortiMail
will not be able to send emails to Office 365. This is because the access control rule
specifies which IP addresses or domains are allowed to relay emails through FortiMail.
D. A Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center has not been set properly to
the FortiMail Cloud FQDN.
If the Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center is not set properly to the
FortiMail Cloud FQDN, then Office 365 will not be able to send emails to FortiMail. This is
because the Mail Flow connector specifies which SMTP server is used to send emails to
external recipients.
Refer to the exhibit.
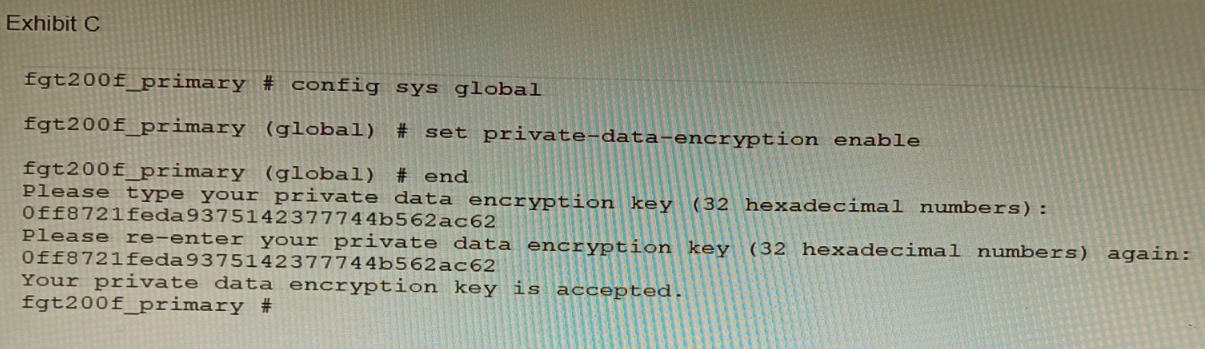
A customer has deployed a FortiGate 200F high-availability (HA) cluster that contains &
TPM chip. The exhibit shows output from the FortiGate CLI session where the
administrator enabled TPM.
Following these actions, the administrator immediately notices that both FortiGate high
availability (HA) status and FortiManager status for the FortiGate are negatively impacted.
What are the two reasons for this behavior? (Choose two.)
A. The private-data-encryption key entered on the primary did not match the value that the TPM expected.
B. Configuration for TPM is not synchronized between FortiGate HA cluster members.
C. The FortiGate has not finished the auto-update process to synchronize the new configuration to FortiManager yet.
D. TPM functionality is not yet compatible with FortiGate HA D The administrator needs to manually enter the hex private data encryption key in FortiManager
Explanation: The two reasons for the negative impact on the FortiGate HA status and
FortiManager status after enabling TPM are:
The private-data-encryption key entered on the primary unit did not match the
value that the TPM expected. This could happen if the TPM was previously
enabled and then disabled, and the key was changed in between. The TPM will
reject the new key and cause an error in the configuration synchronization.
Configuration for TPM is not synchronized between FortiGate HA cluster
members. Each cluster member must have the same private-data-encryption key
to form a valid HA cluster and synchronize their configurations. However, enabling
TPM on one unit does not automatically enable it on the other units, and the key
must be manually entered on each unit. To resolve these issues, the administrator
should disable TPM on all units, clear the TPM data, and then enable TPM again
with the same private-data-encryption key on each unit.
| Page 2 out of 12 Pages |
| Previous |