
- Email support@dumps4free.com

A company's NOC personnel have a custom Python script they run manually by logging
into each VM to fix a common issue across all of the corporate VMs. Management has no
audit history of who is running the script or when it is occurring. The company has recently
implemented Calm and management has asked its administrators to accomplish these
tasks:
Reduce the manual effort for the NOC personnel.
Ensure the process is repeatable across all applications.
Provide audit history for management of the actions.
Which two actions should the administrators take to accomplish these tasks? (Choose
two.)
A. Create a new Action, Add an Execute task with a script type of EScript, paste the custom script into the action
B. View the Execution History tab under the Runbook page for audit purposes
C. Create a new Runbook Add an Execute task with a script type of EScript paste the custom script into the action
D. View the Audit tab under the Application view for audit purposes
A company wants to ensure that all developers are able to request new development
environments on demand by using ServiceNow.
The administrator notices that even though developers create new environments, they
rarely remove these environments when moving on to new assignments. Today, the
administrator has gone into Prism Central to check when the VM was created, in order to
reach out to the developer and ask if it can be deleted. The administrator has accidentally
deleted the wrong VM in the past.
Which two methods can the administrator use to automate this task to avoid deleting the incorrect VMs? (Choose two.)
A. Create a playbook REST API action to delete the VM from a ServiceNow approval flow.
B. Create a playbook webhook action to delete the VM from a ServiceNow approval flow.
C. Create a playbook webhook trigger to delete the VM from a ServiceNow approval flow.
D. Create a playbook REST API trigger to delete the VM from a ServiceNow approval flow.
An administrator has a Linux VM that does batch processing out of a queue. Currently, a
technician connects to the VM console and runs a command on the VM to initiate or
terminate the batch processing application, as there is no programmatic interface for the
application.
The application is processor intensive, so it should only run outside of business hours. The
VM has the ability to send REST API calls to Prism.
How should the administrator configure a Playbook to satisfy the needs of this process with
minimal external interaction?
A. Manual Trigger > Power On > VM SSH > Wait for Some Time > Power Off VM
B. Time Trigger > VM SSH > Wait for Some Time > VM SSH
C. Webhook Trigger > REST API > Wait for Some Time > REST API
D. Manual Trigger > VM SSH > Wait for Some Time > VM SSH
Refer to the exhibit.
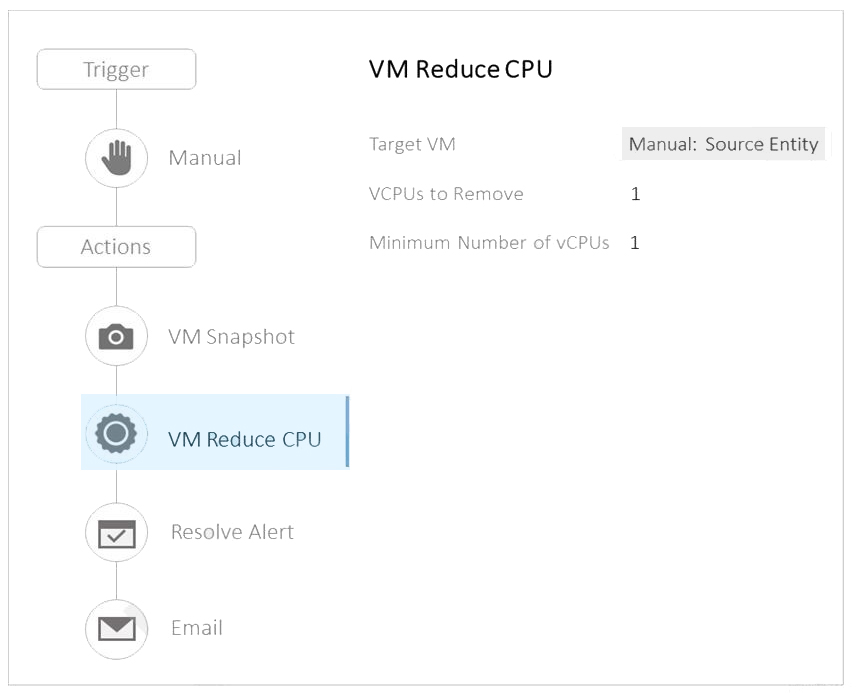
An administrator created the Playbook shown in the exhibit to allow for manual reduction of
vCPU count on any selected VM within their environment. During a test run of the play on
one of the VMs running in development, the administrator ran into an error that the
Playbook cannot be completed against the selected VM.
Here are the details of the affected VM:
VM Name: VM2
vCPU: 4
RAM: 8 GB
OS: Windows 2016
Hypervisor: AHV
What caused this Playbook to fail?
A. This play cannot be executed against a VM on AHV.
B. The VM needs to be powered off before vCPU can be reduced.
C. Reduction of vCPU cannot be done on a VM with a running snapshot.
D. The play will cause the VM to go below the minimum vCPU.
An administrator had provided Linux VM console access to the OS Team. However, the
team is unable to access one of the newly-created Linux VMs.
How can the administrator resolve this issue?
A. Create a local user in Linux OS and provide access to the OS Team.
B. Provide Prism Admin access to the OS Team Active Directory Group.
C. Create a role for the OS Team Active Directory Group and add the VMs to it.
D. Assign new VMs to a category and provide category access to the OS Team.
| Page 2 out of 15 Pages |
| Previous |