
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 5: Mix Questions
You have an Azure subscription that contains a user named User1.
You need to ensure that User1 can deploy virtual machines and manage virtual networks.
The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which role-based access control (RBAC) role should you assign to User1?
A.
Owner
B.
Virtual Machine Administrator Login
C.
Contributor
D.
Virtual Machine Contributor
Virtual Machine Contributor
To ensure that User1 can deploy virtual machines and manage virtual networks, you need to assign an RBAC role that grants the necessary permissions to perform these tasks. The solution must also use the principle of least privilege, which means that you should only grant the minimum level of access required to accomplish the goal. Based on these requirements, the best RBAC role to assign to User1 is D. Virtual Machine Contributor. This role allows User1 to create and manage virtual machines, disks, snapshots, and network interfaces. It also allows User1 to connect virtual machines to existing virtual networks and subnets. However, it does not allow User1 to create or delete virtual networks or subnets, or to access the virtual machines themselves. This role follows the principle of least privilege by limiting User1’s access to only the resources and actions that are relevant to deploying virtual machines and managing virtual networks1.
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the resources shown in the following table.
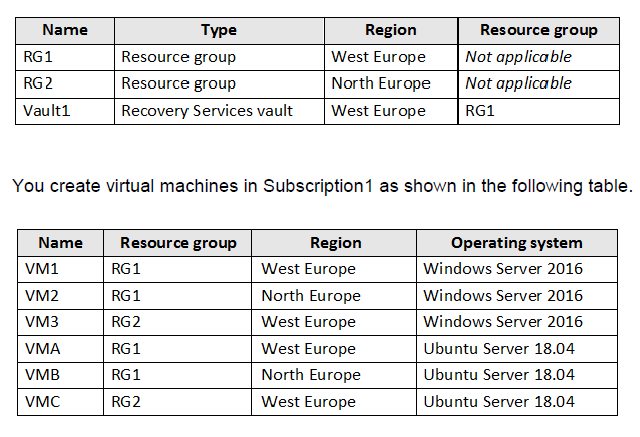
You plan to use Vault1 for the backup of as many virtual machines as possible. Which virtual machines can be backed up to Vault1?
A.
VM1, VM3, VMA, and VMC only
B.
VM1 and VM3 only
C.
VM1, VM2, VM3, VMA, VMB, and VMC
D.
VM1 only
E.
VM3 and VMC only
VM1, VM3, VMA, and VMC only
Explanation:
To create a vault to protect virtual machines, the vault must be in the same region as the virtual machines. If you have virtual machines in several regions, create a Recovery Services vault in each region.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-cyrl-ba/azure/backup/backup-create-rs-vault
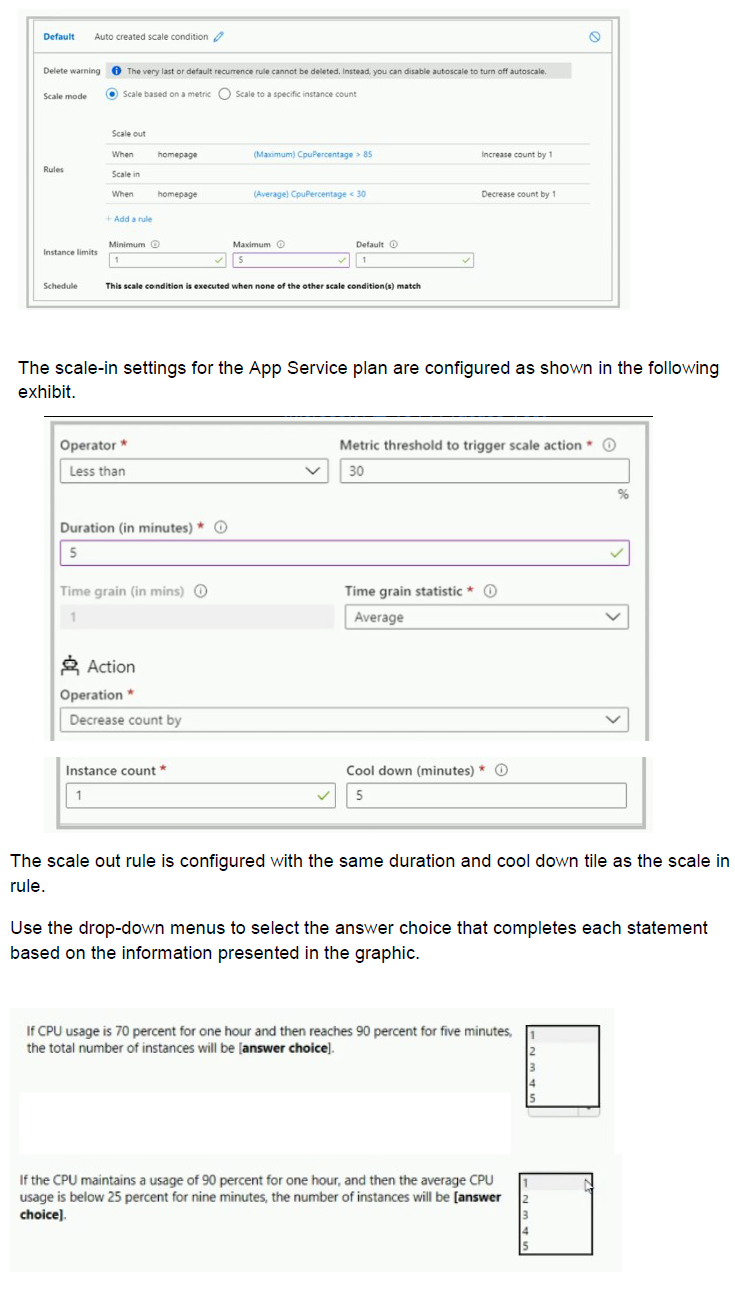
You have the App Service plan shown in the following exhibit.

You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual networks shown in the following table.
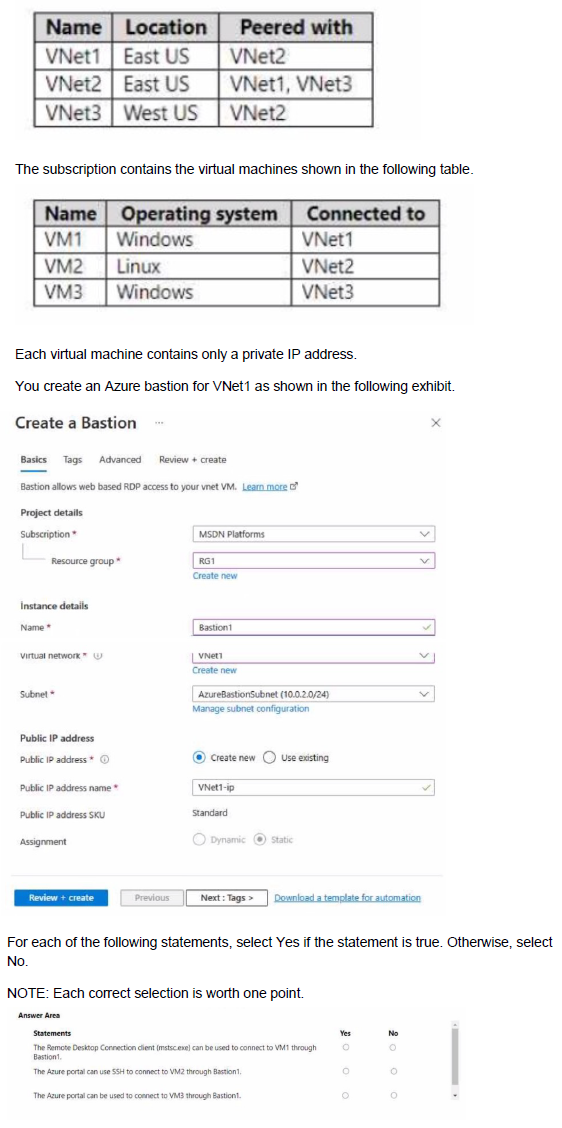
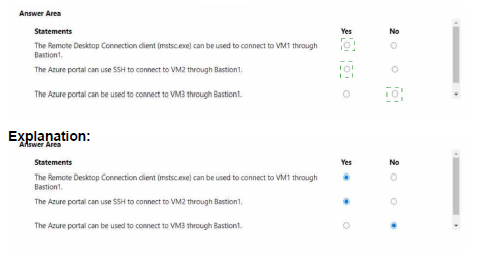
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 and an Azure key vault named Vault1. On VM1, you plan to configure Azure Disk Encryption to use a key encryption key (KEK) You need to prepare Vault! for Azure Disk Encryption.
Which two actions should you perform on Vault1? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A.
Create a new key.
B.
Select Azure Virtual machines for deployment
C.
Configure a key rotation policy.
D.
Create a new secret.
E.
Select Azure Disk Encryption for volume encryption
Create a new key.
Configure a key rotation policy.
Explanation:
To prepare Vault1 for Azure Disk Encryption, you need to perform the following actions on Vault1:
Create a new key. A key encryption key (KEK) is an encryption key that is used to encrypt the encryption secrets before they are stored in the key vault. You can create a new KEK by using the Azure CLI, the Azure PowerShell, or the Azure portal1. You can also import an existing KEK from another source, such as a hardware security module (HSM)2. The KEK must be a 2048-bit RSA key or a 256-bit AES key3.
Select Azure Disk Encryption for volume encryption. This is an advanced access policy setting that enables Azure Disk Encryption to access the keys and secrets in the key vault. You can select this setting by using the Azure CLI, the Azure PowerShell, or the Azure portal4. You must also enable access to Microsoft Trusted Services if you have enabled the firewall on the key vault.
| Page 1 out of 64 Pages |