
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 1: Exam Pool A
What is the output of this code?

A.
username Cisco
B.
get_credentials
C.
username
D.
CISCO
CISCO

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Refer to the exhibit.
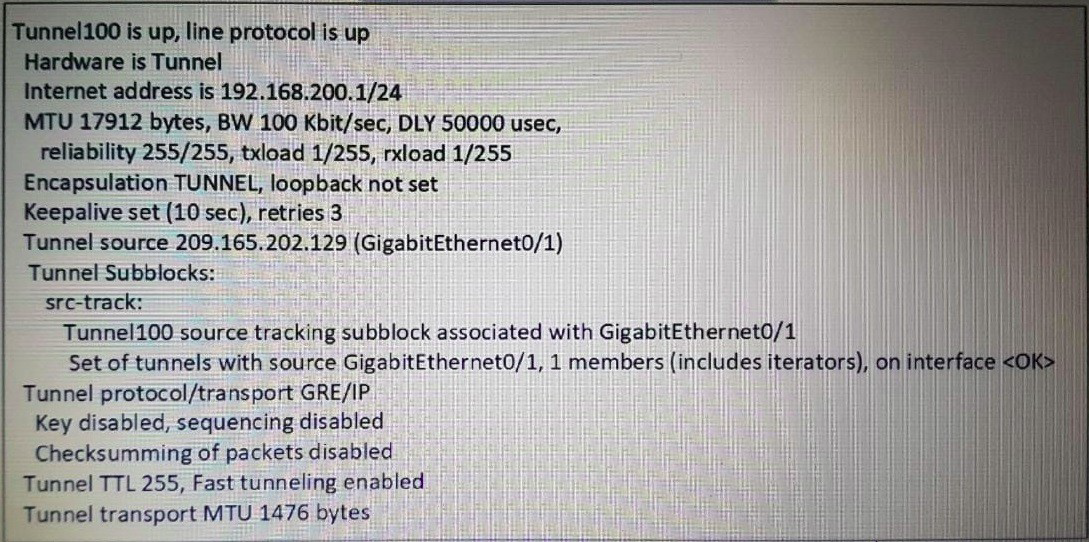
A network engineer configures a GRE tunnel and enters the show Interface tunnel command. What does the output confirm about the configuration?
A.
The keepalive value is modified from the default value.
B.
Interface tracking is configured.
C.
The tunnel mode is set to the default
D.
The physical interface MTU is 1476 bytes.
The tunnel mode is set to the default
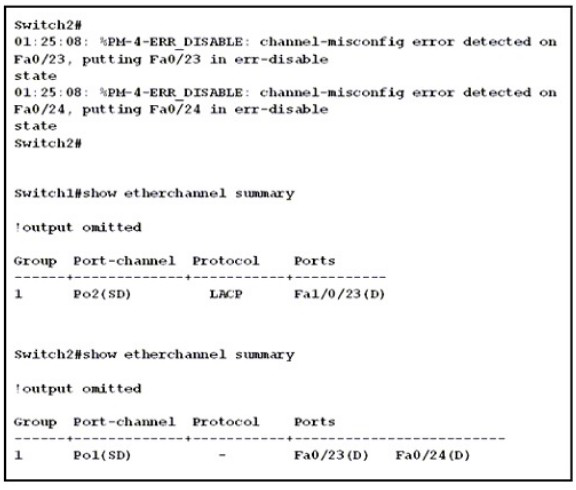
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is configuring an EtherChannel between Switch1 and Switch2 and notices the console message on switch2. Based on the output, which action resolves this issue?
A.
Configure less member ports on Switch2.
B.
Configure the same port channel interface number on both switches
C.
Configure the same EtherChannel protocol on both switches
D.
Configure more member ports on Switch1.
Configure the same EtherChannel protocol on both switches
Explanation: In this case, we are using your EtherChannel without a negotiation protocol on Switch2. As a result, if the opposite switch is not also configured for EtherChannel operation on the respective ports, there is a danger of a switching loop. The EtherChannel Misconfiguration Guard tries to prevent that loop from occuring by disabling all the ports bundled in the EtherChannel.
Which TCP setting is tuned to minimize the risk of fragmentation on a GRE/IP tunnel?
A.
MTU
B.
Window size
C.
MRU
D.
MSS
MSS
Explanation: The TCP Maximum Segment Size (TCP MSS) defines the maximum amount of data that a host is willing to accept in a single TCP/IP datagram. This TCP/IP datagram might be fragmented at the IP layer. The MSS value is sent as a TCP header option only in TCP SYN segments. Each side of a TCP connection reports its MSS value to the other side. Contrary to popular belief, the MSS value is not negotiated between hosts. The sending host is required to limit the size of data in a single TCP segment to a value less than or equal to the MSS reported by the receiving host.
TCP MSS takes care of fragmentation at the two endpoints of a TCP connection, but it does not handle the case where there is a smaller MTU link in the middle between these two endpoints. PMTUD was developed in order to avoid fragmentation in the path between the endpoints.
| Page 16 out of 168 Pages |
| Previous |