
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 1: Exam Pool A
What did the following commands determine?
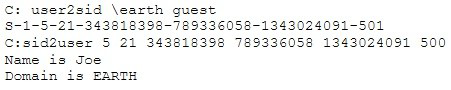
A.
That the Joe account has a SID of 500
B.
These commands demonstrate that the guest account has NOT been disabled
C.
These commands demonstrate that the guest account has been disabled
D.
That the true administrator is Joe
E.
Issued alone, these commands prove nothing
That the true administrator is Joe
Which of the following statements about a zone transfer is correct? (Choose three.)
A.
A zone transfer is accomplished with the DNS
B.
A zone transfer is accomplished with the nslookup service
C.
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a DNS server maintains
D.
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a nslookup server maintains
E.
A zone transfer can be prevented by blocking all inbound TCP port 53 connections
F.
Zone transfers cannot occur on the Internet
A zone transfer is accomplished with the DNS
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a DNS server maintains
A zone transfer can be prevented by blocking all inbound TCP port 53 connections
A zone file consists of which of the following Resource Records (RRs)?
A.
DNS, NS, AXFR, and MX records
B.
DNS, NS, PTR, and MX records
C.
SOA, NS, AXFR, and MX records
D.
SOA, NS, A, and MX records
SOA, NS, A, and MX records
User A is writing a sensitive email message to user B outside the local network. User A has
chosen to use PKI to secure his message and ensure only user B can read the sensitive
email. At what layer of the OSI layer does the encryption and decryption of the message
take place?
A.
Application
B.
Transport
C.
Session
D.
Presentation
Presentation
Explanation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Presentation_layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and
serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer. The
presentation layer is responsible for the formatting and delivery of information to the
application layer for further processing or display.
Encryption is typically done at this level too, although it can be done on the application,
session, transport, or network layers, each having its own advantages and disadvantages.
Decryption is also handled at the presentation layer. For example, when logging on to bank
account sites the presentation layer will decrypt the data as it is received.
What is a NULL scan?
A.
A scan in which all flags are turned off
B.
A scan in which certain flags are off
C.
A scan in which all flags are on
D.
A scan in which the packet size is set to zero
E.
A scan with an illegal packet size
A scan in which all flags are turned off
| Page 24 out of 114 Pages |
| Previous |