
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 2, Exam Pool B
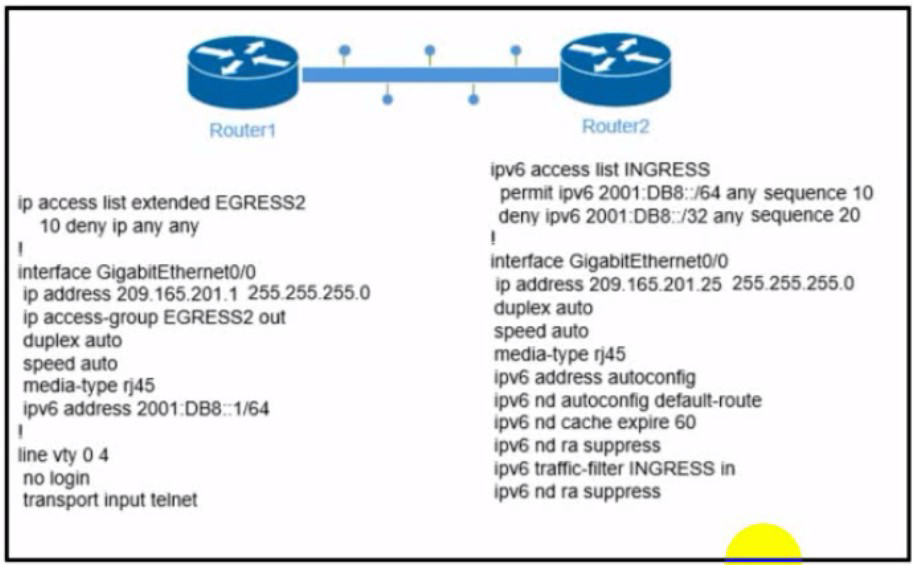
Refer to the exhibit. The engineer configured and connected Router2 to Router1. The link came up but could not establish a Telnet connection to Router1 IPv6 address of 2001:DB8::1. Which configuration allows Router2 to establish a Telnet connection to Router1?
A.
jpv6 unicast-routing
B.
permit ICMPv6 on access list INGRESS for Router2 to obtain IPv6 address
C.
permit ip any any on access list EGRESS2 on Router1
D.
IPv6 address on GigabitEthernet0/0
IPv6 address on GigabitEthernet0/0
Explanation: -------------R1-----------------------
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.0
ip access-group EGRESS2 out
ipv6 address 2001:DB8::1/64
end
-----------R2-------------------------
Refer to the exhibit.

When monitoring an IPv6 access list, an engineer notices that the ACL does not have any hits and is causing unnecessary traffic to pass through the interface Which command must be configured to resolve the issue?
A.
access-class INTERNET in
B.
ipv6 traffic-filter INTERNET in
C.
ipv6 access-class INTERNET in
D.
ip access-group INTERNET in
ipv6 access-class INTERNET in
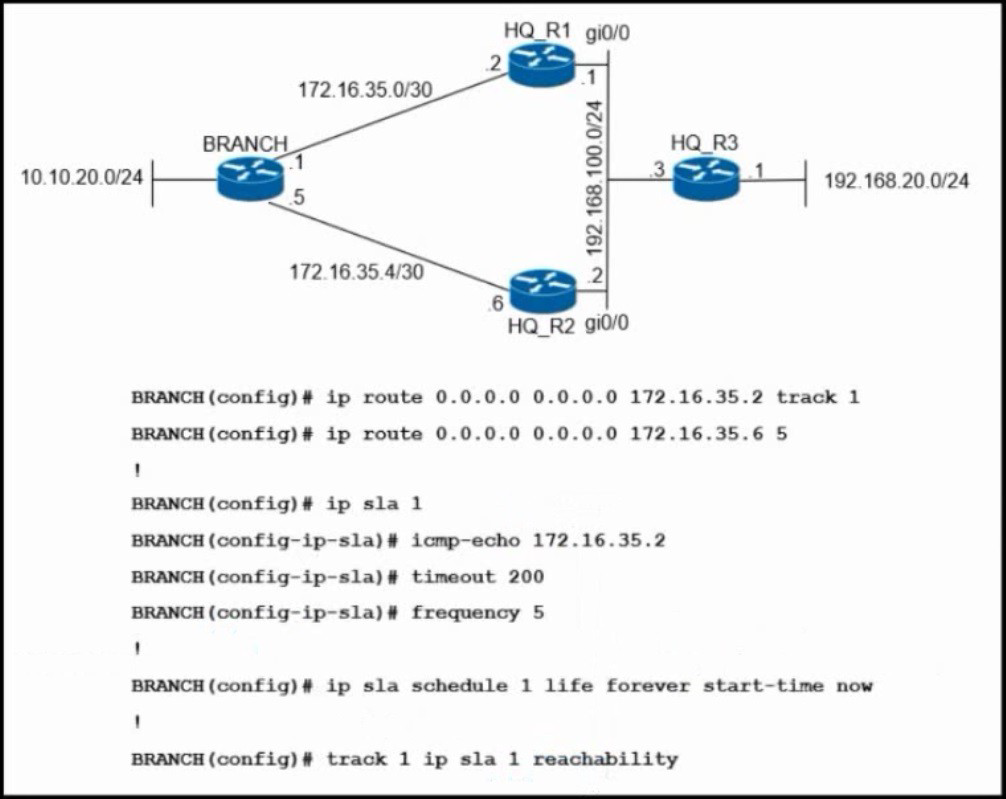
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer has successfully set up a floating static route from the BRANCH router to the HQ network using HQ_R1 as the primary default gateway When the g0/0 goes down on HQ_R1, the branch network cannot reach the HQ network 192.168.20.0/24. Which set of configurations resolves the issue?
A.
HQ_R3(config)# ip sla responder
HQ_R3(config)# ip sla responder icmp-echo 172.16.35.1
B.
BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 192.168.100.2
C.
HQ R3(config)# Ip sla responder
HQ R3(config)# Ip sla responder Icmp-echo 172.16.35.5
D.
BRANCH(config)# Ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sta)# Icmp-echo 192.168.100.1
BRANCH(config)# Ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sta)# Icmp-echo 192.168.100.1
Exhibit:
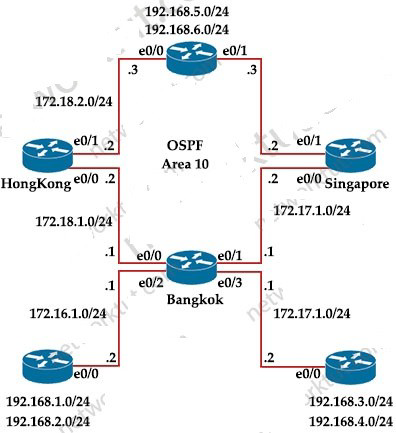
Bangkok is using ECMP to reach to the 192.168.5.0/24 network. The administrator must configure Bangkok in such a way that Telnet traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 and192.168.4.0/24 networks uses the HongKong router as the preferred router. Which set of configurations accomplishes this task?
A.
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
interface Ethernet0/3
ip policy route-map PBR1
B.
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
interface Ethernet0/1
ip policy route-map PBR1
C.
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
!
interface Ethernet0/3
ip policy route-map PBR1
D.
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip policy route-map PBR1
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
!
interface Ethernet0/3
ip policy route-map PBR1
Explanation: We need to use Policy Based Routing (PBR) here on Bangkok router to match the traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 & 192.168.4.0/24 and “set ip next-hop” to HongKong router(172.18.1.2 in this case).
Note: Please notice that we have to apply the PBR on incoming interface e0/3 to receive traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 and 192.168.4.0/24.
Refer to the exhibit.
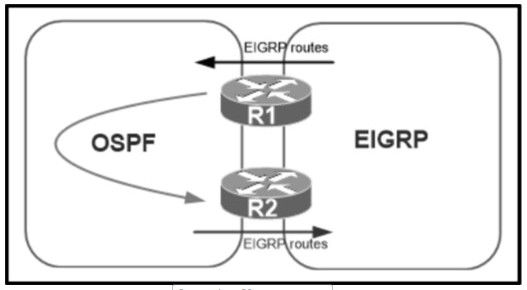
A network administrator configured mutual redistribution on R1 and R2 routers, which caused instability in the network. Which action resolves the issue?
A.
Set a tag in the route map when redistributing EIGRP into OSPF on R1. and match the same tag on R2 to allow when redistributing OSPF into EIGRP.
B.
Apply a prefix list of EIGRP network routes in OSPF domain on R1 to propagate back into the EIGRP routing domain.
C.
Set a tag in the route map when redistributing EIGRP into OSPF on R1, and match the same tag on R2 to deny when redistributing OSPF into EIGRP.
D.
Advertise summary routes of EIGRP to OSPF and deny specific EIGRP routes when redistributing into OSPF.
Set a tag in the route map when redistributing EIGRP into OSPF on R1, and match the same tag on R2 to deny when redistributing OSPF into EIGRP.
| Page 34 out of 113 Pages |
| Previous |