
- Email support@dumps4free.com

Topic 2, Exam Pool B
Refer to the exhibit.

The network administrator configured the branch router for IPv6 on the
E 0/0 interface The neighboring router is fully configured to meet requirements, but the neighbor relationship is not coming up. Which action fixes the problem on the branch router to bring the IPv6 neighbors up?
A.
Enable the IPv4 address family under the E 0/0 interface by using the address-family Ipv4 unicast command
B.
Disable IPv6 on the E 0/0 interface using the no ipv6 enable command
C.
Enable the IPv4 address family under the router ospfv3 4 process by using the addressfamily ipv4 unicast command
D.
Disable OSPF for IPv4 using the no ospfv3 4 area 0 ipv4 command under the E 0/0 interface.
Enable the IPv4 address family under the router ospfv3 4 process by using the addressfamily ipv4 unicast command
Once again, Cisco changed the IOS configuration commands required for OSPFv3 configuration. The new OSPFv3 configuration uses the “ospfv3” keyword instead ofthe earlier “ipv6 router ospf” routing process command and “ipv6 ospf” interface commands. The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may havetwo processes per interface, but only one process per address family (AF).
Which feature drops packets if the source address is not found in the snooping table?
A.
IPv6 Source Guard
B.
IPv6 Destination Guard
C.
IPv6 Prefix Guard
D.
Binding Table Recovery
IPv6 Source Guard
Refer to Exhibit.
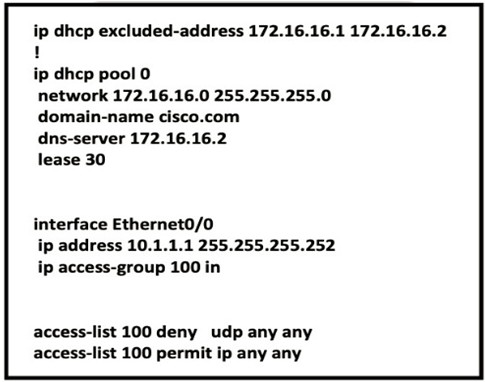
Which two configurations allow clients to get dynamic ip addresses assigned?
A.
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 61 as the first line
B.
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 86 as the first line
C.
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 68 as the first line
D.
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 69 as the first line
E.
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 67 as the first line
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 68 as the first line
Configure access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 67 as the first line
Refer to the exhibit.
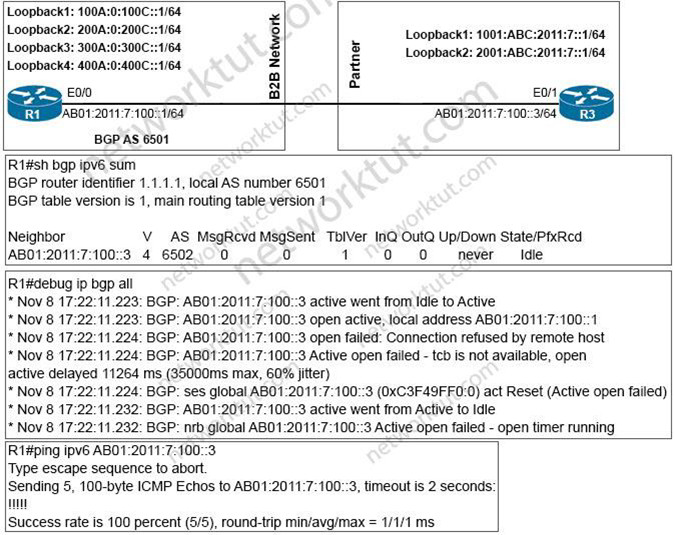
An engineer configured BGP between routers R1 and R3 The BOP peers cannot establish neighbor adjacency to be able to exchange routes. Which configuration resolves this issue?
A.
R3
router bgp 6502
address-family ipv6
neighbor AB01:2011:7:100::1 activate
B.
R1
router bgp 6501
address-family ipv6
neighbor AB01:2011:7:100;:3 activate
C.
R3
router bgp 6502
neighbor AB01:2011:7:100::1 ebgp-muttlhop 255
D.
R1
router bgp 6501 neighborAB01:2011:7:100::3ebgp-multihop255
R3
router bgp 6502
address-family ipv6
neighbor AB01:2011:7:100::1 activate
Refer to exhibit.
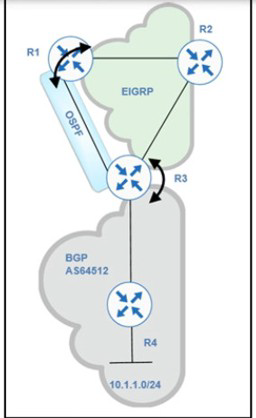
Routing protocols are mutually redistributed on R3 and R1. Users report intermittent connectivity to services hosted on the 10.1.1.0/24 prefix. Significant routing update changes are noticed on R3 when the show ip route profile
command is run. How must the services be stabilized?
A.
The issue with using BGP must be resolved by using another protocol and redistributing it into EIGRP on R3
B.
The routing loop must be fixed by reducing the admin distance of iBGP from 200 to 100 on R3
C.
The routing loop must be fixed by reducing the admin distance of OSPF from 110 to 80 on R3
D.
The issue with using iBGP must be fixed by running eBGP between R3 and R4
The routing loop must be fixed by reducing the admin distance of iBGP from 200 to 100 on R3
| Page 23 out of 113 Pages |
| Previous |